接着上一节分析,我们知道@Aspect的解析,发生在BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder类中,那么这个类是何方神圣呢?
它在注解中写道:帮助@Aspecj bean from BeanFactory 进行解析,并且建立Advisors。用来auto -proxying。
1.初始化:
在AbstractAutoProxyCreator在refresh()第六步中进行getBean(),注入到BeanPostProcessor容器中的时候,进行了实例化and初始化,而它的子类的初始化方法:
protected void initBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {super.initBeanFactory(beanFactory);if (this.aspectJAdvisorFactory == null) {this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = new ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory(beanFactory);}this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder =new BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilderAdapter(beanFactory, this.aspectJAdvisorFactory);
}public BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder(ListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AspectJAdvisorFactory advisorFactory{this.beanFactory = beanFactory;this.advisorFactory = advisorFactory;
}
这里就new了一个builder,传入的参数,重点是第二个:ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory类:
结构简单:
2.成员:
private final ListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
//advisos解析助手
private final AspectJAdvisorFactory advisorFactory;private volatile List<String> aspectBeanNames;
private final Map<String, List<Advisor>> advisorsCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<String, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory> aspectFactoryCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
它的字段存放了BeanFactory,还存放了解析的AspectJ bean,还有对于的Advisor,我们这里重点就是通过AdvisorFactory如何解析出Advisor,这里先看一下什么是Advisor:
Advice:对应增强的方法 参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/6c1b73b54c46
Advisor:关联了Advice和Pointcut。上起到了连接点的匹配下起到了通知类型的调用。统一了拦截的调用过程。
Advised:关联了Advisor和TargetSource的类。AOP进行方法拦截的时候,就是从它里面获取的拦截调用链。
单词:advice 通知,建议 advisor 顾问
它在本类中使用的实现类:InstantiationModelAwarePoincutAdvisorImpl类
它的字段丰富:
private final AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut;
private final Class<?> declaringClass;
//代表一个方法,方法的数据信息
private final String methodName;
private final Class<?>[] parameterTypes;
private transient Method aspectJAdviceMethod;
//两个工厂
private final AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory;
private final MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory;private final int declarationOrder;
private final String aspectName; //@Aspect通知类的名字private final Pointcut pointcut; //联系Pointcut
private final boolean lazy;
private Advice instantiatedAdvice; //联系Adviceprivate Boolean isBeforeAdvice;
private Boolean isAfterAdvice;
3.解析过程:
在builder的build()方法中核心部分:
if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) { //找到@Aspect 注解的beanaspectNames.add(beanName);AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {//封装MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);//获得 类中的方法 【入】List<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);}
可见调用advisorFactory进行解析:传入的是BeanFactory和beanName的封装,里面解析出了AspectMetadata信息,在这个类构造的时候进行解析的。
public List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();validate(aspectClass);//再一次封装MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();//解析获得Advisorfor (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) { //获得所有方法,除去@pointcutAdvisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName); //【入】if (advisor != null) {advisors.add(advisor);}}//advisors为空if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);}// 处理@Aspect中的字段
@DeclareParents的使用:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f7238613c877for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);if (advisor != null) {advisors.add(advisor);}}return advisors;
}
在解析过程中,对于普通method来说,解析比较简单,封装成advice即可,而对于pointcut的解析,稍显复杂,所以我们重点放在了pointcut的解析上面。
1.getAdvisorMethods()
排除掉@pointcut方法,剩下本类的方法,+Object定义的很多方法
private List<Method> getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass) {final List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>();ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, method -> {//如果不是@Pointcut方法,则添加if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {methods.add(method);}});methods.sort(METHOD_COMPARATOR);return methods;
}
使用doWithMethods()对方法进行遍历,然后设置回调函数,并且要遍历父类的方法,递归调用:
public static void doWithMethods(Class<?> clazz, MethodCallback mc, @Nullable MethodFilter mf) {// Keep backing up the inheritance hierarchy.Method[] methods = getDeclaredMethods(clazz);for (Method method : methods) {if (mf != null && !mf.matches(method)) {continue;}try {mc.doWith(method); //回调--> 保存method}}if (clazz.getSuperclass() != null) {doWithMethods(clazz.getSuperclass(), mc, mf); //递归父类}else if (clazz.isInterface()) { //接口for (Class<?> superIfc : clazz.getInterfaces()) {doWithMethods(superIfc, mc, mf);}}
}
2.getAdvisor()【重点】
对方法进行遍历处理,
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());//获取 切点表达式AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());if (expressionPointcut == null) {return null;}//查看返回的类型,也就是Advisor的实现类return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
}
【注意】这里传入的是任何method,除了pointcut方法,那么这里的获取切点 表达式,并不是实际的切点表达式,而是5个通知标签里面的value,该value指名了使用那个切点。
private AspectJExpressionPointcut getPointcut(Method candidateAdviceMethod, Class<?> candidateAspectClass) {AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod); //找AspectJAnnotation注解if (aspectJAnnotation == null) {return null;}//创建AspectJExpressionPointcut ajexp =new AspectJExpressionPointcut(candidateAspectClass, new String[0], new Class<?>[0]);ajexp.setExpression(aspectJAnnotation.getPointcutExpression()); //设置表达式if (this.beanFactory != null) {ajexp.setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);}return ajexp;
}
findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(),观察这个方法,是否实现了集合中的某个注解,找到了就封装返回。
protected static AspectJAnnotation<?> findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(Method method) {for (Class<?> clazz : ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES) { //集合,装了6个注解AspectJAnnotation<?> foundAnnotation = findAnnotation(method, (Class<Annotation>) clazz);if (foundAnnotation != null) {return foundAnnotation;}}return null;
}
//上述的常量集合:
private static final Class<?>[] ASPECTJ_ANNOTATION_CLASSES = new Class<?>[] {Pointcut.class, Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class};
跟入(跳过一级):find(),调用工具类进行find
public static <A extends Annotation> A findAnnotation(Method method, @Nullable Class<A> annotationType) {Assert.notNull(method, "Method must not be null");if (annotationType == null) {return null;}//先从缓存中获取AnnotationCacheKey cacheKey = new AnnotationCacheKey(method, annotationType);A result = (A) findAnnotationCache.get(cacheKey);//缓存未击中if (result == null) {//解析 是否是桥接方法,Method resolvedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);//findresult = findAnnotation((AnnotatedElement) resolvedMethod, annotationType); //【入】if (result == null) {result = searchOnInterfaces(method, annotationType, method.getDeclaringClass().getInterfaces());}Class<?> clazz = method.getDeclaringClass();while (result == null) { //遍历父类....}if (result == null) {result = searchOnInterfaces(method, annotationType, clazz.getInterfaces());}}if (result != null) {result = synthesizeAnnotation(result, method); //桥接方法处理findAnnotationCache.put(cacheKey, result); //保存}}return result;
}
BridgedMethod:https://www.jianshu.com/p/250030ea9b28
其实就是一个反射就搞定了,搞这么麻烦,主要是情况没有找到的情况下,还需要处理什么父类等等情况,确保不漏掉。
现在找到了point 表达式,其实不仅仅是找表达式,还有判断method,是否存在五个通知的注解,再从五个通知里面找到表达式,也就是注解的value值。
现在找到了开始封装advisor
回到ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory类的getAdvisor()方法:
return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);
//构造方法片段:
else {// A singleton aspect.this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;this.lazy = false;this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut); //【入】
}
,pointcut表达式,只是简单的保存,没有处理,重点是生成advice类,看一下它的五个实现
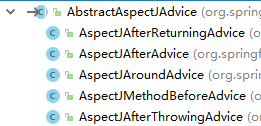
instaniateAdvice进入:
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut) {//【入】Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut,this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);return (advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE);
}
//getAdvice:
....
switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {case AtPointcut:if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");}return null;case AtAround:springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);break;case AtBefore:
.... 五个通知
现在advisor创建完毕。注意PointCut()真实的注解,在这里是没有解析的,也就是说真实的切入点注解并没有解析出来,要等到后面bean,afterBeanPostProcessor()被触发继续分析。