一、MRF-based deformable registration and ventilation estimation of lung CT
1. Introduction:
A. Large motion of small features
Motion within the lungs can often be larger than the scale of the features (vessels and airways). This may cause a registration algorithm to get trapped in a local minimum, and may lead to an erroneous registration. Local minima are frequently encountered in lung registration.
…
An approach to avoid local minima is the use of discrete optimisation, which is usually formulated on a Markov random field (MRF). Discrete optimisation offers numerous advantages, in particular a greater control over the displacement space, to overcome these limitations.
深度学习方法在大变形配准下表现很差,比如肺部的呼吸运动导致的大变形往往比深度学习提取的特征(比如血管和气道)要大,这时候深度学习就容易陷入局部最优的陷阱。
一个避免局部最优陷阱的方法就是使用基于马尔可夫随机场的离散优化方法。
作者提出了一种密集随机采样方法,使用一个带规则控制点网格的参数 B-spline 变换模型。假设以控制点为中心的非重叠立方体中的体素以相同的平移向量移动。为了降低相似度损失的计算复杂性,只对一个立方体中所有体素的随机样本进行计算。
基于离散优化的可变形配准通常表示为马尔可夫随机场(MRF)标记。在他们的参数化的图像配准框架中,定义了一个图,其中节点 p 对应于均匀 B-spline 中的控制点,每个节点有一组标签 f p f_p fp?,对应于离散位移。
他们的相似度损失函数度量一个控制点 p 周围的体素以及另一幅图上相同控制点的位置的体素的相似度,控制点 p 内的体素的位移 f p f_p fp? 不会受周围的控制点内的体素影响。
配准的流程
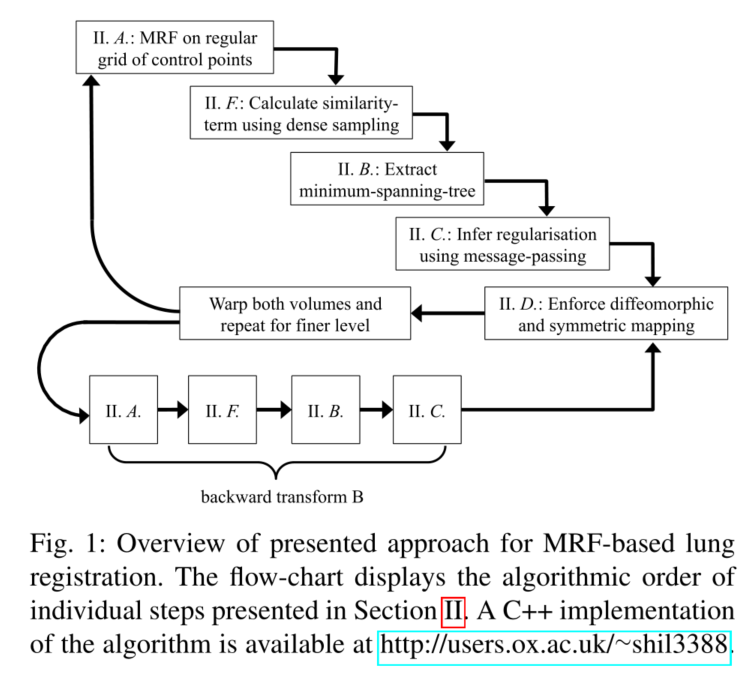
离散控制点组成的最小生成树

利用普利姆算法,我们可以快速找到给定一组节点 p 和边 e 的唯一 MST
作者预计,在三维位移空间上进行完全采样是不必要的,为了达到 SOTA 的结果,减少标签和内存的使用将导致更广泛地采用离散 DLIR。