Lab5: xv6 lazy page allocation
原文地址:YSBLOG
参考资料:
https://juejin.cn/post/7034359064121311240
https://blog.miigon.net/posts/s081-lab5-lazy-page-allocation/
实验目的:实现延迟分配用户空间堆内存,在调用sbrk()的时候,不立即分配内存,而是当内存页面真正被访问时才进行实际的物理内存分配。
为了方便总结,这次一起把三个任务同时完成。
首先修改sys_sbrk()让其在调用时不实际分配内存,而是进行记录。
// sysproc.c
uint64
sys_sbrk(void)
{
int addr;int n;if(argint(0, &n) < 0)return -1;addr = myproc()->sz;myproc()->sz += n; // 只增加sz的数值大小,不实际分配内存if (n < 0) {
// n小于0的情况为释放内存,立即执行uvmdealloc(myproc()->pagetable, addr, myproc()->sz);}// if(growproc(n) < 0)// return -1;return addr;
}
修改后,运行系统执行echo hi,结果如下:
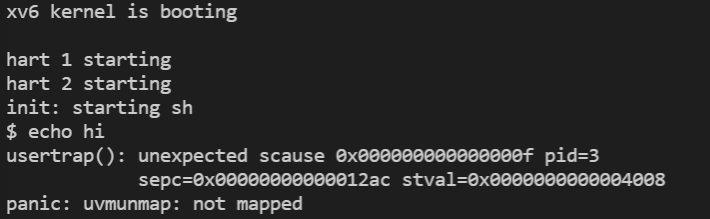
如图所示,执行echo hi后我们得到了一个page fault,是因为在Shell中执行程序,Shell会先fork一个子进程,子进程会通过exec执行echo,而这个过程中会先sys_sbrk()申请一些内存,但因为我们修改了代码,这个没有实际分配内存,所以出错了。通过错误信息可以看到,此时SCAUSE寄存器的值为15,表面这是一个store page fault,同时pid为3,这时Shell的pid,SPEC中保存进入内核前的pc地址为0x12ac,STVAL寄存器保存出错的虚拟地址0x4008。
第二步,完成惰性内存分配的实现。在vm.c中实现lazyalloc,记得在defs.h中添加声明。在执行惰性内存分配时需要确认当前地址是否是由于惰性内存分配而导致的缺页。
uint64 lazyalloc(struct proc *p, uint64 va) {
pte_t *pte; // 虚拟地址的页表现if (va < p->sz // 虚拟地址小于当前进程逻辑上分配的地址大小&& PGROUNDDOWN(va) != r_sp() // 虚拟地址不能位于栈底的页面,因为栈底的页面存在一个guard page不能访问,用于检测stack overflow错误&& ( ((pte = walk(p->pagetable, va, 0)) == 0) || ((*pte & PTE_V) == 0)) // 页表项当前不存在) {
char* mem = kalloc(); // 分配一页内存if (mem == 0) {
printf("lazy alloc : out of memory\n");p->killed = 1;} else {
memset(mem, 0, PGSIZE);// 将申请的物理内存与虚拟地址进行映射if (mappages(p->pagetable, PGROUNDDOWN(va), PGSIZE,(uint64)mem, PTE_W|PTE_X|PTE_R|PTE_U) != 0) {
// 映射失败printf("lazy alloc : failed to map page\n");kfree(mem);p->killed = 1;}return (uint64)mem;}}return 0;
}
第三步,需要在实际访问内存时判端,若存在缺页,则调用lazyalloc。
这里的处理方式与lab4差不多,可以通过r_scause()在陷入时判断陷入的原因,若下入的原因为13则为读缺页,若陷入原因为15为写缺页。
// trap.c
void
usertrap(void)
{
... ...} else if((which_dev = devintr()) != 0){
// ok} else if ((r_scause() == 13 || r_scause() == 15)) {
// 当读缺页或者写缺页引起中断时,进行惰性内存分配if (lazyalloc(p, r_stval()) <= 0) {
p->killed = 1;}} else {
printf("usertrap(): unexpected scause %p pid=%d\n", r_scause(), p->pid);printf(" sepc=%p stval=%p\n", r_sepc(), r_stval());p->killed = 1;}... ...
}// vm.c
uint64
walkaddr(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 va)
{
pte_t *pte;uint64 pa;if(va >= MAXVA)return 0;pte = walk(pagetable, va, 0);if ((pte == 0) ||((*pte & PTE_V) == 0) || ((*pte & PTE_U) == 0)) {
// 缺页时进行惰性内存分配if ((pa = lazyalloc(myproc(), va)) <= 0) {
// 惰性内存分配失败pa = 0;}} else {
pa = PTE2PA(*pte);}return pa;
}
第四步,解决painc。由于原本的xv6中没有惰性分配策略,所以当页面在映射、拷贝以及取消映射时检测到页面权限不正确或者访问失败时会进行painc报错,但在加入惰性分配策略后,页面在未实际读写数据之前可能并不存在,所以我们需要忽略对应的painc(这并不影响拷贝和映射的执行的正确性)。
// vm.c
int
mappages(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 va, uint64 size, uint64 pa, int perm)
{
uint64 a, last;pte_t *pte;a = PGROUNDDOWN(va);last = PGROUNDDOWN(va + size - 1);for(;;){
if((pte = walk(pagetable, a, 1)) == 0)return -1;// 忽视页面权限问题,直接进行映射// if(*pte & PTE_V) // panic("remap");*pte = PA2PTE(pa) | perm | PTE_V;if(a == last)break;a += PGSIZE;pa += PGSIZE;}return 0;
}
// vm.c
void
uvmunmap(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 va, uint64 npages, int do_free)
{
uint64 a;pte_t *pte;if((va % PGSIZE) != 0)panic("uvmunmap: not aligned");for(a = va; a < va + npages*PGSIZE; a += PGSIZE){
// 跳过不存在的页面if((pte = walk(pagetable, a, 0)) == 0)// panic("uvmunmap: walk");continue;if((*pte & PTE_V) == 0)// panic("uvmunmap: not mapped");continue;if(PTE_FLAGS(*pte) == PTE_V)panic("uvmunmap: not a leaf");if(do_free){
uint64 pa = PTE2PA(*pte);kfree((void*)pa);}*pte = 0;}
}
// vm.c
int
uvmcopy(pagetable_t old, pagetable_t new, uint64 sz)
{
pte_t *pte;uint64 pa, i;uint flags;char *mem;for(i = 0; i < sz; i += PGSIZE){
// 跳过不存在的页面if((pte = walk(old, i, 0)) == 0)continue;// panic("uvmcopy: pte should exist");if((*pte & PTE_V) == 0)continue;// panic("uvmcopy: page not present");pa = PTE2PA(*pte);flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte);if((mem = kalloc()) == 0)goto err;memmove(mem, (char*)pa, PGSIZE);if(mappages(new, i, PGSIZE, (uint64)mem, flags) != 0){
kfree(mem);goto err;}}return 0;err:uvmunmap(new, 0, i / PGSIZE, 1);return -1;
}
使用echo hi,lazytests,usertests进行测试,结果如下:
xv6 kernel is bootinghart 1 starting
hart 2 starting
init: starting sh
$ echo hi
hi
$ lazytests
lazytests starting
running test lazy alloc
test lazy alloc: OK
running test lazy unmap
test lazy unmap: OK
running test out of memory
test out of memory: OK
ALL TESTS PASSED
$ usertests
usertests starting
lazy alloc : out of memory
test execout: lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
lazy alloc : out of memory
OK
test copyin: OK
test copyout: OK
test copyinstr1: OK
test copyinstr2: OK
test copyinstr3: OK
test rwsbrk: OK
test truncate1: OK
test truncate2: OK
test truncate3: OK
test reparent2: OK
test pgbug: OK
test sbrkbugs: usertrap(): unexpected scause 0x000000000000000c pid=3305sepc=0x0000000000005580 stval=0x0000000000005580
OK
test badarg: OK
test reparent: OK
test twochildren: OK
test forkfork: OK
test forkforkfork: OK
test argptest: OK
test createdelete: OK
test linkunlink: OK
test linktest: OK
test unlinkread: OK
test concreate: OK
test subdir: OK
test fourfiles: OK
test sharedfd: OK
test exectest: OK
test bigargtest: OK
test bigwrite: OK
test bsstest: OK
test sbrkbasic: lazy alloc : out of memory
OK
test sbrkmuch: OK
test kernmem: OK
test sbrkfail: lazy alloc : out of memory
OK
test sbrkarg: OK
test validatetest: OK
test stacktest: OK
test opentest: OK
test writetest: OK
test writebig: OK
test createtest: OK
test openiput: OK
test exitiput: OK
test iput: OK
test mem: lazy alloc : out of memory
OK
test pipe1: OK
test preempt: kill... wait... OK
test exitwait: OK
test rmdot: OK
test fourteen: OK
test bigfile: OK
test dirfile: OK
test iref: OK
test forktest: OK
test bigdir: OK
lazy alloc : out of memory
ALL TESTS PASSED
$