List:
① List容器是有序的collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对List容器中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。List容器允许插入重复的值,包括null;
② 最常见的两个List接口的实现类是ArrayList和LinkedList;
ArrayList及常用API:
① ArrayList—动态数组;
② ArrayList类扩展了AbstractList并实现了List接口;
③ 支持可随需增长的动态数组;
④ ArrayList构造方法:
a) ArrayList()
b) ArrayList(Collection c)
c) ArrayList(int capacity)
⑤ 除了继承的方法外,ArrayList常用方法:
a) E get(int index) 返回此列表中指定位置上的元素
b) int indexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含元素,则返回 -1。
c) ……
ArrayList新增,修改,输出
1 List<String> nList = new ArrayList<String>(); 2 nList.add("zhangsan");// 将指定的元素添加到此列表的尾部 3 nList.add("lisi"); 4 nList.add("wangwu"); 5 nList.add(1, "jay");// 将指定的元素插入此列表中的指定位置 6 nList.set(0, "Ali");// 用指定的元素替代此列表中指定位置上的元素 7 System.out.println("使用迭代器对象来进行统一的遍历"); 8 Iterator<String> it = nList.iterator(); 9 while (it.hasNext()) {10 String name = it.next();11 System.out.println(name);12 }13 14 System.out.println("使用增强for循环来进行统一的遍历");15 for(String name:nList){16 System.out.println(name);17 }输出结果为:
使用迭代器对象来进行统一的遍历
Ali
jay
lisi
wangwu
使用增强for循环来进行统一的遍历
Ali
jay
lisi
wangwu
接上面测试常用方法:
1 System.out.println("****************************************"); 2 System.out.println(nList.indexOf("lisi"));//返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含元素,则返回 -1。 3 System.out.println(nList.remove("lisi"));//移除此列表中首次出现的指定元素(如果存在)。 4 System.out.println(nList.remove(0));//移除此列表中指定位置上的元素 5 System.out.println(nList.size());//返回此列表中的元素数。--原本有4个,上面删除了2个。结果为2 6 System.out.println(nList.contains("zhangsan"));//如果此列表中包含指定的元素,则返回 true。 7 System.out.println(nList.get(0));//返回此列表中指定位置上的元素。 8 System.out.println(nList.isEmpty());//如果此列表中没有元素,则返回 true 9 nList.clear();//移除此列表中的所有元素10 System.out.println(nList.isEmpty());输出结果:
****************************************
2
true
Ali
2
false
jay
false
true
新建一个类,添加
1 class Student{2 private String name;3 private int age;4 }为其添加get,set方法
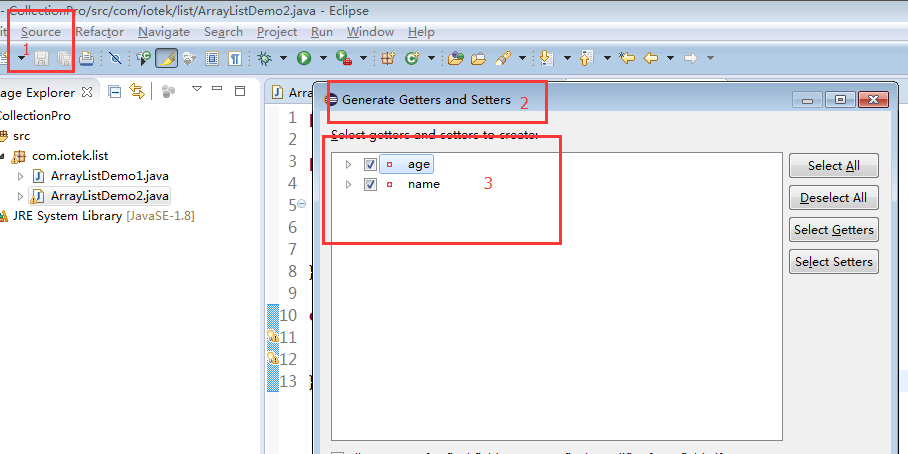
将会自动创建get,set方法
1 public String getName() { 2 return name; 3 } 4 public void setName(String name) { 5 this.name = name; 6 } 7 public int getAge() { 8 return age; 9 }10 public void setAge(int age) {11 this.age = age;12 }为其创建带2个参数的构造方法
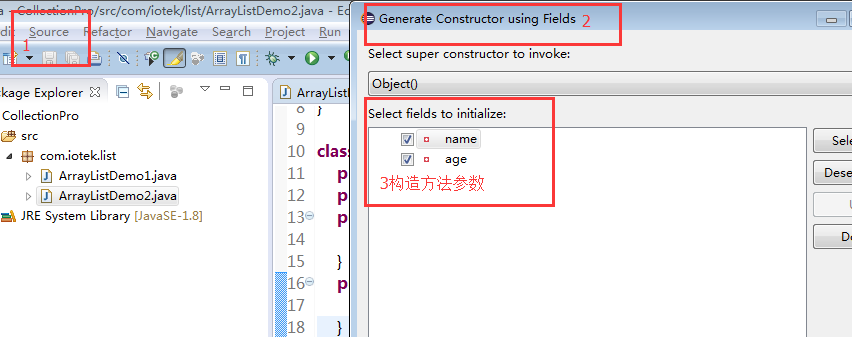
1 public Student(String name, int age) {2 super();3 this.name = name;4 this.age = age;5 }在主方法中添加元素及操作
1 List<Student> stuList=new ArrayList<Student>(); 2 Student stu1=new Student("zhangsan", 10); 3 Student stu2=new Student("lisi", 20); 4 Student stu3=new Student("wangwu", 30); 5 Student stu4=new Student("zhaoliu", 25); 6 Student stu5=new Student("tianqi", 15); 7 stuList.add(stu1); 8 stuList.add(stu2); 9 stuList.add(stu3);10 stuList.add(stu4);11 stuList.add(stu5);12 Student stu6=new Student("tianqi", 15);13 System.out.println(stuList.indexOf(stu6));//-1但我们想要返回当名字与年龄相同时就返回索引;
查看ArrayList中的indexOf方法如下:(查看方法ctrl+鼠标左键选中ArrayList,再在大纲视图中找到indexOf(Object)方法):
1 public int indexOf(Object o) { 2 if (o == null) { 3 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 4 if (elementData[i]==null) 5 return i; 6 } else { 7 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 8 if (o.equals(elementData[i])) 9 return i;10 }11 return -1;12 }此处用的equals比较,说明student每创建一个都不可能会相同,所以我们要重构Student类中的equals方法;
在Eclipse中也提供了重构equals的方法:
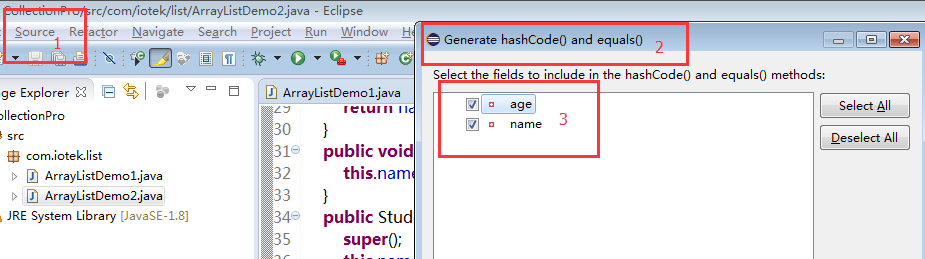
1 @Override 2 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 3 if (this == obj) 4 return true; 5 if (obj == null) 6 return false; 7 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 8 return false; 9 Student other = (Student) obj;10 if (age != other.age)11 return false;12 if (name == null) {13 if (other.name != null)14 return false;15 } else if (!name.equals(other.name))16 return false;17 return true;18 }修改好Student类之后再进行测试:
1 System.out.println(stuList.indexOf(stu6));//-12 System.out.println(stuList.contains(stu6));3 System.out.println(stuList.remove(stu6));//remove中用equals方法删除,所有会将stu5一并删除4 System.out.println(stuList.indexOf(stu5));5 System.out.println(stuList.size());未重构equals()之前,输出结果为:
-1
false
false
4
5
重构了equals ()之后,再输出:
输出结果为:
4
true
true
-1
4