hiredis 是 redis 的client端C语言 lib, hiredis拥有同步和异步的API, 异步API的实现有多种方法,分别依赖libev, libevent, libuv, ae等等,其中ae是redis内部实现的一个异步事件处理模块。
稍微修改了hiredis的example-ae.c代码:在一个线程里面循环10次执行命令ping, 检查redisserver, 如下所示, 线程发完10次ping后,调用disconnect, 发现aeMain函数并未退出,程序一直阻塞住.
#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <signal.h>#include <thread>#include<functional>#ifdef __cplusplus extern "C"{#endif#include <hiredis.h>#include <async.h>#include <adapters/ae.h>#ifdef __cplusplus }#endif/* Put event loop in the global scope, so it can be explicitly stopped */static aeEventLoop *loop;void getCallback(redisAsyncContext *c, void *r, void *privdata) { redisReply *reply = r; if (reply == NULL) return; printf("argv[%s]: %s\n", (char*)privdata, reply->str);}void connectCallback(const redisAsyncContext *c, int status) { if (status != REDIS_OK) { printf("Error: %s\n", c->errstr); aeStop(loop); return; } printf("Connected...\n");}void disconnectCallback(const redisAsyncContext *c, int status) { if (status != REDIS_OK) { printf("Error: %s\n", c->errstr); aeStop(loop); return; } printf("Disconnected...\n"); aeStop(loop);}void quitConnCallBack(redisAsyncContext *c, void *r, void *privdata) { printf("quit"); redisAsyncDisconnect(c);}void testThreadLoop(void * p) { static int num = 10; char c11[64]; strcpy(c11, "test"); while(1) { std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1500)); num--; if (num < 0) { //在这里调用disconnect, 并不能使aeMain退出 redisAsyncDisconnect((redisAsyncContext *)p); //正确做法,应该调用如下 //redisAsyncCommand((redisAsyncContext *)p, quitConnCallBack, c11, "quit"); printf("exit\n"); return; } redisAsyncCommand((redisAsyncContext *)p, getCallback, c11, "ping"); }}int main (int argc, char **argv) { signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); redisAsyncContext *c = redisAsyncConnect("127.0.0.1", 6379); if (c->err) { /* Let *c leak for now... */ printf("Error: %s\n", c->errstr); return 1; } loop = aeCreateEventLoop(64); redisAeAttach(loop, c); redisAsyncSetConnectCallback(c,connectCallback); redisAsyncSetDisconnectCallback(c,disconnectCallback); std::thread t(testThreadLoop, c); t.detach(); aeMain(loop); return 0;}
首先检查下两个主要函数aeStop, aeMain的逻辑:
aeStop, aeMain函数代码如下:
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { eventLoop->stop = 0; while (!eventLoop->stop) { if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL) eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop); aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS); }}void aeStop(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { eventLoop->stop = 1;}
1. stop分析
aeStop仅设置stop标志为true, aeMain里面在一直循环处理事件,第一印象是,直接设了stop为true后,aeMain在处理完事件后,跳出aeProcessEvents函数后,检查stop为true就会跳出while循环。但是事实是aeMain并未跳出循环,难道因为是不同线程间操作,要将stop设置为volatile类型?尝试修改了stop为volatile int类型,测试结果:aeMain 仍然未推出,程序阻塞,无法推出。
2.aeProcessEvents分析
这时就只能推测由于aeProcessEvents没有退出,导致aeMain执行无法检测stop值,分析该函数,推测可能阻塞在aeApiPoll函数,同时发现tvp变量是个NULL, 查看aeApiPoll代码(ae_epoll.c),如下
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags){ //... //tvp 会是NULL, 推测阻塞在aeApiPoll, 查看aeApiPoll代码进行证实 numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp); for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd]; int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask; int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd; int rfired = 0; /* note the fe->mask & mask & ... code: maybe an already processed * event removed an element that fired and we still didn't * processed, so we check if the event is still valid. */ if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) { rfired = 1; fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); } if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) { if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc) fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask); } processed++; } } /* Check time events */ if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop); return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */}static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp) { aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata; int retval, numevents = 0; //真相在这边,epoll_wait, 第三个参数为-1, epoll_wait将一直等待下去! retval = epoll_wait(state->epfd,state->events,eventLoop->setsize, tvp ? (tvp->tv_sec*1000 + tvp->tv_usec/1000) : -1); if (retval > 0) { int j; numevents = retval; for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { int mask = 0; struct epoll_event *e = state->events+j; if (e->events & EPOLLIN) mask |= AE_READABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLOUT) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLERR) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; if (e->events & EPOLLHUP) mask |= AE_WRITABLE; eventLoop->fired[j].fd = e->data.fd; eventLoop->fired[j].mask = mask; } } return numevents;}
整理下aeMain的流程如下图所示,
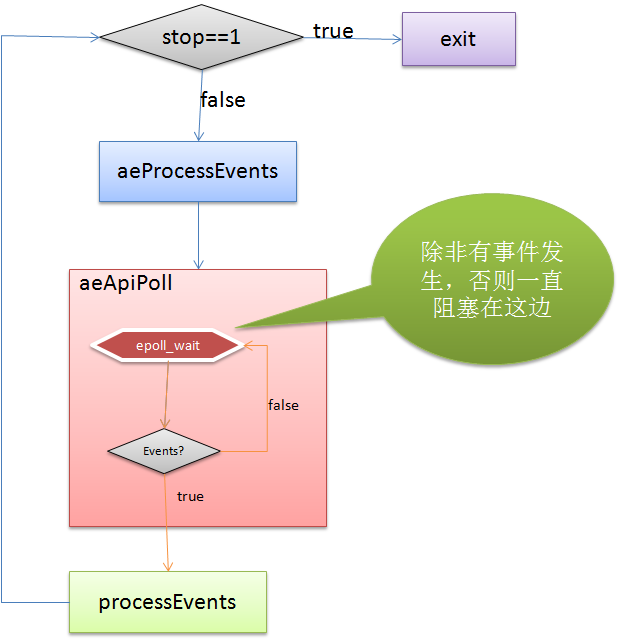
我们的disconnect回调, 内部调用 aeStop函数,如果刚好发生在processEvents之后,aeMain检查stop值之前,那么就没问题,当然这种概率极其小,如果这都中了,那可以买彩票了~~,现在我们知道aestop调用是有立即生效的限制范围,我们最好在processEvents的时候,判断是否应该退出aeMain, 如果是就调用aeStop. processEvents内部会调用到我们外部定义的各种命令的回调函数, 刚好redis有个quit的命令(让redisserver关闭连接), 我们就增加一个quit命令回调函数调用aeStop:
redisAsyncCommand((redisAsyncContext *)p, quitConnCallBack, c11, "quit");
void quitConnCallBack(redisAsyncContext *c, void *r, void *privdata) { printf("quit"); redisAsyncDisconnect(c);}