自定义控件是一些android程序员感觉很难攻破的难点,起码对我来说是这样的,但是我们可以在网上找一些好的博客关于自定义控件好好拿过来学习研究下,多练,多写点也能找到感觉,把一些原理弄懂,今天就讲下自定义组合控件,这个特别适合在标题栏或者设置界面,看下面图:

就非常适合使用组合控件了,现在写一个玩玩:
activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:hy="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.example.customcircle" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <com.example.customcircle.SettingView android:id="@+id/sv1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" hy:title = "标题1" hy:content = "内容1" ></com.example.customcircle.SettingView> <com.example.customcircle.SettingView android:id="@+id/sv2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" hy:title = "标题2" hy:content = "内容2" ></com.example.customcircle.SettingView> <com.example.customcircle.SettingView android:id="@+id/sv3" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" hy:title = "标题3" hy:content = "内容3" ></com.example.customcircle.SettingView></LinearLayout>
SettingView.java
public class SettingView extends RelativeLayout { private TextView title; private TextView content; public SettingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) { super(context, attrs, defStyle); initView(context); } public SettingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); initView(context); /** * 获取一个样式的属性集 * 把布局文件xml中的获取到的样式集合attrs跟自己自定义的样式集合建立一个映射关系 */ TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.SettingView); String title = a.getString(0); String content = a.getString(1); //设置到界面上 setTitle(title); setContent(content); a.recycle(); } public SettingView(Context context) { super(context); initView(context); } private View initView(Context context){ View view = View.inflate(context, R.layout.setting_view, this); title = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.title); content = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.content); return view; } public void setTitle(String tilte){ title.setText(tilte); } public void setContent(String strContent){ content.setText(strContent); } public void setTextSize(int size){ content.setTextSize(size); title.setTextSize(size); }}setting_view.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="#22000000"
>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:layout_below="@id/title"
/>
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/cb"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
<View
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="1px"
android:background="#000000"
android:layout_below="@id/cb"
/>
</LinearLayout>
hy:title = "标题1"
hy:content = "内容1"
这个时候xml文件会报错
<!-- Text color. -->
<attr name="textColor" />
<!-- Size of the text. Recommended dimension type for text is "sp" for scaled-pixels (example: 15sp). -->
<attr name="textSize" />
<!-- Style (bold, italic, bolditalic) for the text. -->
<attr name="textStyle" />
<!-- Typeface (normal, sans, serif, monospace) for the text. -->
<attr name="typeface" />
<!-- Color of the text selection highlight. -->
<attr name="textColorHighlight" />
<!-- Color of the hint text. -->
<attr name="textColorHint" />
<!-- Color of the links. -->
<attr name="textColorLink" />
</declare-styleable>
运行效果:
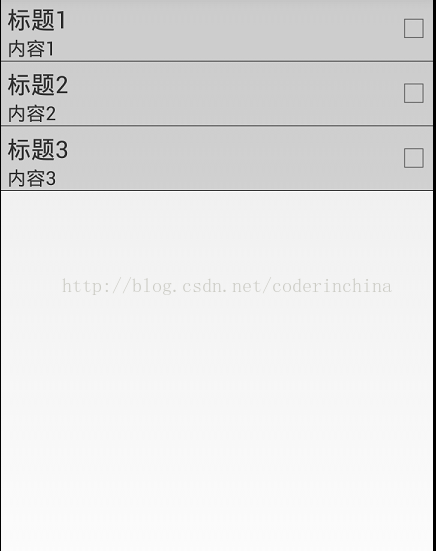
总结下自定义组合控件的步骤:
1. 写一个类 继承 ViewGroup LinearLayout RelativeLayout
2. 如果在布局文件里面定义view对象 使用这个view对象的两个参数的构造方法.
3. 定义这个自定义控件里面要显示的内容
View.inflate(context, R.layout.ui_setting_view, this);
4. 添加自定义控件的属性.
定义自定义属性的命名空间
5. 声明自定义的属性
<declare-styleable name="SettingView">
<attr name="title" format="string" />
<attr name="desc_on" format="string" />
<attr name="desc_off" format="string" />
</declare-styleable>
观察R文件 生成 attr内部类 生成styleable 数组 所有的attrs
6. 在xml布局文件里面配置 自定义的属性.
7. 在自定义view对象的构造方法里面 获取AttributeSet
跟我们自定义的属性建立映射关系
8. 在自定义组合控件里面 设置 布局文件的数据, 扩展点击事件.
9. 在布局文件使用自定义的view对象.