I、逐帧动画
public class AnimationDrawable extends DrawableContainer implements Runnable, Animatable
public class DrawableContainer extends Drawable implements Drawable.Callback
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?><animation-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:oneshot="false"> <item android:drawable="@drawable/icon0" android:duration="500"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/icon1" android:duration="500"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/icon2" android:duration="500"/> <item android:drawable="@drawable/icon3" android:duration="500"/></animation-list>
android:oneshot为false时表示循环播放,默认为false
myImageView=(ImageView)findViewById(R.id.myImageView);myImageView.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.myanimation); AnimationDrawable animationDrawable =(AnimationDrawable) myImageView.getBackground();animationDrawable.start();//animationDrawable.stop();
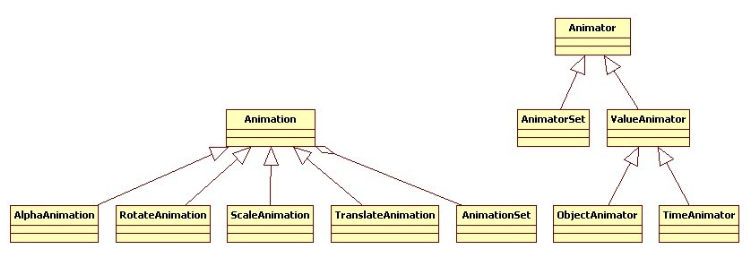
二、扩展知识:AnimationDrawable类
1、提供函数:
public void start()public void stop()public boolean isRunning()public int getNumberOfFrames()public Drawable getFrame(int index)public int getDuration(int i)public boolean isOneShot()public void setOneShot(boolean oneShot)/**Add a frame to the animation */public void addFrame(Drawable frame, int duration)
2、已定义了一个帧动画,如何做到播放其中的某几个连续帧;(比如本文中有4个帧,播放2-3帧)
分析:AnimationDrawable类提供了getFrame和getDuration方法,但是未提供相应的setter函数来控制播放的帧位置。AnimationDrawable类中有一个私有变量mCurFrame表示当前的播放帧。定义如下:
/** The current frame, may be -1 when not animating. */ private int mCurFrame = -1;
public class MyImageView extends ImageView{ private AnimationDrawable animationDrawable; public MyImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.myanimation); animationDrawable = (AnimationDrawable) getBackground(); setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { animationDrawable.start(); } }); } @Override public void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { try { Field field = AnimationDrawable.class.getDeclaredField("mCurFrame"); field.setAccessible(true); int curFrame = field.getInt(animationDrawable); if(curFrame == 2) field.setInt(animationDrawable, 0); } catch(Exception e) { Log.e("AnimationDrawable", e.toString()); } super.onDraw(canvas); } }II、补间动画:
<!-- 缩放 --> <scale android:fromXScale="0.0" android:toXScale="1.0" android:fromYScale="0.0" android:toYScale="1.0" android:pivotX="50%" android:pivotY="50%" android:duration="1000" android:repeatCount="-1" android:repeatMode="reverse" /> <!-- fromXScale:沿X,Y轴的缩放比例 from-to--> <!-- pivotX:缩放的中心点位置,(占View大小的百分比) --> <!-- duration:持续时间 --> <!-- repeatCount:重复次数,默认为0,代表旋转一次;则设为n,旋转n+1次;设为-1或infinite,则为无限循环 --> <!-- repeatMode:重复模式,默认为restart-->
Animation animation =AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this,R.anim.anim_set); myImageView.startAnimation(animation);
ScaleAnimation animation = new ScaleAnimation(0, 1, 0, 1); animation.setDuration(1000); animation.setRepeatCount(-1); animation.setRepeatMode(Animation.RESTART); myImageView.startAnimation(animation);
下面用法大同小异:
2、透明度alpha --- AlphaAnimation
<!-- 透明度 --> <alpha android:fromAlpha="0.0" android:toAlpha="1.0" android:duration="1000" android:repeatCount="-1" android:repeatMode="reverse" />
<!-- 旋转 --> <rotate android:fromDegrees="0" android:toDegrees="360" android:pivotX="50%" android:pivotY="50%" android:duration="1000" android:repeatCount="2" android:repeatMode="restart" />
<!-- 移动 --> <translate android:fromXDelta="0" android:toXDelta="1000" android:fromYDelta="0" android:toYDelta="1000" android:duration="1000" />
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?><set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator" android:repeatMode="reverse" android:repeatCount="2" > <!-- 移动 --> <translate android:fromXDelta="0" android:toXDelta="1000" android:fromYDelta="0" android:toYDelta="1000" android:duration="1000" /> <!-- 缩放 --> <scale android:fromXScale="0.0" android:toXScale="1.0" android:fromYScale="0.0" android:toYScale="1.0" android:pivotX="50%" android:pivotY="50%" android:duration="1000" /> <!-- 透明度 --> <alpha android:fromAlpha="0.0" android:toAlpha="1.0" android:duration="1000" /> <rotate android:fromDegrees="0" android:toDegrees="360" android:pivotX="50%" android:pivotY="50%" android:duration="1000" /></set>
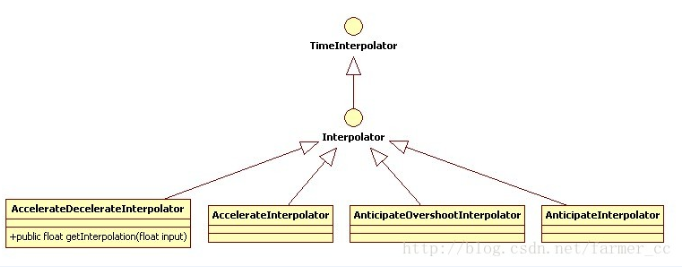
An interpolator where the rate of change starts and ends slowly but accelerates through the middle
An interpolator where the rate of change starts out slowly and and then accelerates.
An interpolator where the change starts backward then flings forward.
An interpolator where the change starts backward then flings forward and overshoots the target value and finally goes back to the final value.
An interpolator where the change bounces at the end.
An interpolator where the rate of change starts out quickly and and then decelerates.
An interpolator where the rate of change is constant
An interpolator where the change flings forward and overshoots the last value then comes back.
三、添加动画监听器 AnimationListener
animation.setAnimationListener(new AnimationListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) { Log.i("AnimationListener", "动画开始"); } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) { Log.i("AnimationListener", "动画重复"); } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) { Log.i("AnimationListener", "动画结束"); } });<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?><layoutAnimation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:delay="1.0" android:animationOrder="random" android:animation="@anim/anim_set" /> <!-- delay 子类动画时间间隔(延迟) --><!-- animationOrder 子类的显示方式: normal(0 默认) reverse(1 倒序) random(2 随机) --><!-- animation : 对应动画 -->
android:layoutAnimation="@anim/layout_anim"
<为ListView(ViewGroup的子类)添加动画>
String[] mMenuItemStr = { "Bear", "Bird", "Cat", "Tigers", "Panda" ,"Bear", "Bird", "Cat", "Tigers", "Panda"}; listView.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, R.layout.item_left_menu,mMenuItemStr)); Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, R.anim.anim_set); LayoutAnimationController controller = new LayoutAnimationController(animation); controller.setOrder(LayoutAnimationController.ORDER_NORMAL); controller.setDelay(1); listView.setLayoutAnimation(controller);5、ViewGroup第一次进行布局时加载布局动画。可以通过listView.scheduleLayoutAnimation();强制其再次执行
6、添加动画监听:
listView.setLayoutAnimationListener(new AnimationListener() { @Override publicvoid onAnimationStart(Animation animation) { } @Override publicvoid onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) { } @Override publicvoid onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) { } });private Animation animation1, animation2; privateclass myAnimationListener implements AnimationListener { @Override publicvoid onAnimationStart(Animation animation) { } @Override publicvoid onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) { if(animation.hashCode() == animation1.hashCode()) myImageView.startAnimation(animation2); else myImageView.startAnimation(animation1); } @Override publicvoid onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) { } }animation1 = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.anim1); animation2 = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.anim2); myAnimationListener myAnimationListener = new myAnimationListener(); animation1.setAnimationListener(myAnimationListener); animation2.setAnimationListener(myAnimationListener); myImageView.startAnimation(animation1);
private class myInterpolator implements Interpolator { @Override public float getInterpolation(floatinput) { /**input: 取值范围 0.0-1.0,表示动画的加载进度 * 返回值:<1.0表示还未达到目标点;越接近1.0表示离目标点越近;大于1.0表示动画对象已经超过了目标点**/ if(input <= 0.5) return input * input; else return (1 - input) * (1 - input); } }Animation animation = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(MainActivity.this, R.anim.anim1); animation.setInterpolator(new myInterpolator()); myImageView.startAnimation(animation);
/** * An interpolator where the rate of change starts out slowly and * and then accelerates. * */@HasNativeInterpolatorpublic class AccelerateInterpolator implements Interpolator, NativeInterpolatorFactory { private final floatmFactor; private final doublemDoubleFactor; public AccelerateInterpolator() { mFactor = 1.0f; mDoubleFactor = 2.0; } /** * Constructor * * @param factor Degree to which the animation should be eased. Seting * factor to 1.0f produces a y=x^2 parabola. Increasing factor above * 1.0f exaggerates the ease-in effect (i.e., it starts even * slower and ends evens faster) */ public AccelerateInterpolator(floatfactor) { mFactor = factor; mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor; } public AccelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context.getResources(), context.getTheme(), attrs); } /** @hide */ public AccelerateInterpolator(Resources res, Theme theme, AttributeSet attrs) { TypedArray a; if (theme != null) { a = theme.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator, 0, 0); } else { a = res.obtainAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator); } mFactor = a.getFloat(R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator_factor, 1.0f); mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor; a.recycle(); } public float getInterpolation(float input) { if (mFactor == 1.0f) { return input * input; } else { return (float)Math.pow(input, mDoubleFactor); } } /** @hide */ @Override public long createNativeInterpolator() { return NativeInterpolatorFactoryHelper.createAccelerateInterpolator(mFactor); }}