在上一篇文章中,我们提到了让mybatis直接执行sql语句。
http://xiabin1235910-qq-com.iteye.com/blog/1748886
?
接下来介绍在上一篇文章的基础上,我们如何使用mybatis,以及在编程时,应该注意的事项:
1. 命名规约:
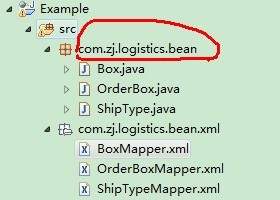
?
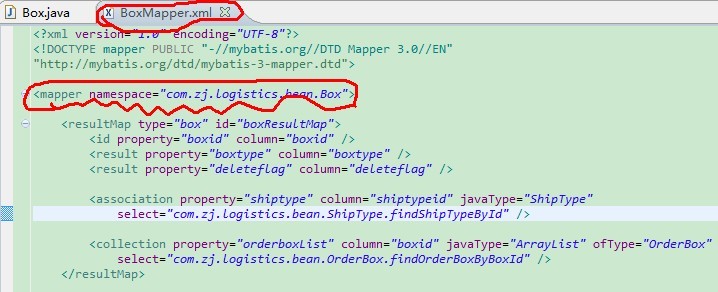
?配置文件的namespace和Box类的路径要一致,我们稍后将会用反射的方式,将Box和BoxMapper串接起来。
?
在项目中采用的普遍做法是,在dao层建立一个泛型基类,这个泛型基类提供一个公用方法,将实体和xml文件对应起来。如图:
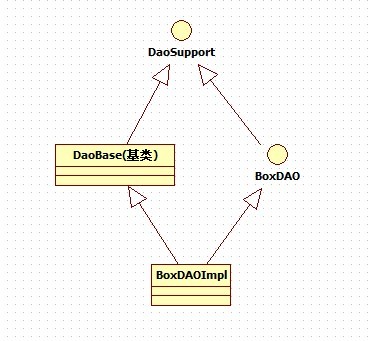
?
好的,介绍一下DaoBase泛型类,首先要将实体和xml串联起来。
public interface DaoSupport<T> { /** * 添加对象 * @param t */ public abstract void add(T t);}?
public class DaoBase<T> implements DaoSupport<T> { @Override public void add(T o) { try { SessionManage.dealSession(SessionMethod.INSERT, getDealMethod(SessionMethod.INSERT).toString(), o); } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("事务异常"); e.printStackTrace(); } } private StringBuilder getDealMethod(SessionMethod sm) { Class<T> c = getDetailClass(); StringBuilder queryMapper = new StringBuilder(c.getName()); queryMapper.append("."); if (sm.equals(SessionMethod.DELETE)) { queryMapper.append(SessionMethod.DELETE.getName()); } else if (sm.equals(SessionMethod.UPDATE)) { queryMapper.append(SessionMethod.UPDATE.getName()); } else { queryMapper.append(SessionMethod.INSERT.getName()); } queryMapper.append(c.getSimpleName()); return queryMapper; } private Class<T> getDetailClass() { Class<T> en; Class c = this.getClass(); // System.out.println(c.getName()); ParameterizedType ptype = null; do { // 遍历所有超类,直到找泛型定义 try { ptype = (ParameterizedType) c.getGenericSuperclass(); } catch (Exception e) { } c = c.getSuperclass(); // System.out.println("super class:" + ptype); } while (ptype == null && c != null); if (ptype == null) { System.out.println("子类中没有定义泛型的具体类型"); } en = (Class<T>) ptype.getActualTypeArguments()[0]; // System.out.println(en.getSimpleName()); return en; }}?其核心思想,就是在泛型类中通过查找出<T> 的 T 的类型,取得T 类的路径, 在sessionManage中将T和 T对应的xml 关联起来,以便完成添加对象的方法。sessionManage的代码,如下:
public class SessionManage { static TransactionFactory transactionFactory = new JdbcTransactionFactory(); public static void dealSession(SessionMethod sm, String queryMethod, Object param) throws SQLException { SqlSession session = MyBatisUtil.getSqlSessionFactory().openSession(); Transaction transaction = transactionFactory.newTransaction( session.getConnection(), false); try { Method m = null; m = session.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(sm.getName(), String.class ,Object.class); if(param instanceof List) { for(Object o : (List)param) { m.invoke(session, queryMethod, o); } } else { m.invoke(session, queryMethod, param); }// int a = 45/0; //生成错误判断是否回滚 //事务提交 transaction.commit(); } catch (SecurityException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (Exception e) { //事务回滚 transaction.rollback(); System.out.println("事务回滚"); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { transaction.close(); session.close(); } }}其核心思想,就是通过反射,将mybatis的session.insert() ? session.update() ? session.delete() 等方法抽象成一个方法。?
?
附:枚举类sessionMethod代码:
public enum SessionMethod { INSERT { @Override public String getName() { return "insert"; } }, UPDATE { @Override public String getName() { return "update"; } }, DELETE { @Override public String getName() { return "delete"; } }; public abstract String getName();}?获取sessionFactory方法:
?
public class MyBatisUtil { private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null; public synchronized static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() { if(sqlSessionFactory == null) { String resource = "mybatis-configuration.xml"; Reader reader = null; try { reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader); } return sqlSessionFactory; }}?以上,仅仅完成了万里长征的第一步,还有更加复杂的查询逻辑等着我们去处理。
这才是我们需要处理的核心内容,也是难点。
?
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
?
相信有了上面的基础,对于我们理解下面的内容有很大帮助。
我们在用自己编写的分页框架,查询语句时,往往需要我们自己去维护这段代码,这就需要我们让mybatis直接执行sql语句。 配置的话 在开头我已经讲过,下面着重讲解使用方式:
?
首先,在做项目时,我们会碰到各种各样的需求,使用软删除,复杂的sql查询语句,表间级联关系查询等等,
所以有必要采用抽象的方式,整合它们。 ?我们先从DaoBase这个基类入手。
?
public class DaoBase<T> implements DaoSupport<T> { @Override public QueryResult<T> getScrollData(long startIndex, long maxResult, String whereSql, Object[] params, LinkedHashMap<String, String> orderBy) { return getAbstractScrollData(startIndex, maxResult, whereSql, params, orderBy, false); } protected QueryResult<T> getAbstractScrollData(long firstIndex, long maxResult, String whereSql, Object[] params, LinkedHashMap<String, String> orderBy, boolean delete) { return getManyToManyScrollData(firstIndex, maxResult, null, whereSql, params, orderBy, delete); } @Override public QueryResult<T> getScrollData(long startIndex, long maxResult, String tableMapping, String whereSql, Object[] params) { return getManyToManyScrollData(startIndex, maxResult, tableMapping, whereSql, params, null, false); } protected QueryResult<T> getManyToManyScrollData(long firstIndex, long maxResult, String tableMapping, String whereSql, Object[] params, LinkedHashMap<String, String> orderBy, boolean delete) { Class<T> c = getDetailClass(); String classNameAll = c.getName(); String className = c.getSimpleName(); StringBuilder sql = getSQL(tableMapping, whereSql, params, orderBy, className, delete); StringBuilder sqlCounts = getCountsSql(tableMapping, whereSql, params, className, delete); sql.append(" ").append("limit ").append(firstIndex).append(", ").append(maxResult); return getQuertResult(classNameAll, sql.toString(), sqlCounts.toString()); } private StringBuilder getSQL(String tableMapping, String whereSql, Object[] params, LinkedHashMap<String, String> orderBy, String className, boolean delete) { StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("select n.* from "); sql.append(className.toLowerCase()).append(" n ") .append(tableMapping == null ? "" : tableMapping + " ") .append("where n.deleteflag=").append(delete ? "1" : "0"); if (whereSql != null) { sql.append(buildWhere(whereSql, params)); } if (orderBy != null) { sql.append(" ").append(buildOrderBy(orderBy)); } return sql; } private QueryResult<T> getQuertResult(String classNameAll, String sql, String sqlCounts) { QueryResult<T> queryResult = new QueryResult<T>(); if (sql != null) { List<T> tlist = SessionManage.getRecordsBySQL(classNameAll, sql); queryResult.setResultList(tlist); } // 分页的结果集需要统计总记录数,否则,不统计 if (sqlCounts != null) { List<String> counts = new ArrayList<String>(); counts = SessionManage.getRecordsOfColumnBySQL(classNameAll, sqlCounts); if (counts != null && counts.size() > 0) { queryResult.setTotalRecord(Long.valueOf(counts.get(0))); } else { queryResult.setTotalRecord(0L); } } return queryResult; }}??
这里的Daobase基类,主要完成了向上层暴露查询分页方法的底层实现。 QueryResult是我们实现的一个分页器,里面存放主要的内容就是 查询集合和总共的集合数量。
?
这里介绍一下两个暴露的方法:
?
getScrollData(long startIndex, long maxResult, String whereSql, Object[] params, LinkedHashMap<String, String> orderBy)
?
?
?
getScrollData(long startIndex, long maxResult, String tableMapping, String whereSql, Object[] params)
?
?
稍加比较,就会发现,第二个方法加入了一个tablemapping参数, 这个参数主要是为了实现表间级联查询所设计的。?
两个方法公用的参数whereSql和params 是为了拼凑where语句使用的。
最后拼凑出来的整体效果如下: select n.* from box n where n.boxtype='xxx' orderby boxid ASC;
?
介绍一下,我们如何使用这个这两个方法,我们在servlet中使用,代码如下:
?
private void getBoxList(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { String pageOfString = request.getParameter("page"); int page; if(pageOfString == null || "".equals(pageOfString)) { page = 1; } else { page = Integer.valueOf(pageOfString); } int maxResult = 10; String selectName = request.getParameter("selectName"); String shiptypeid = request.getParameter("shiptypeid"); QueryResult<Box> qr = new QueryResult<Box>(); StringBuilder wheresql = new StringBuilder("1=1"); List<Object> olist = new ArrayList<Object>(); LinkedHashMap<String, String> orderby = new LinkedHashMap<String,String>(); orderby.put("boxid", "ASC"); if (selectName != null && !selectName.equals("")) { wheresql.append(" and n.boxtype like ?"); olist.add("%" + selectName + "%"); request.setAttribute("selectName", selectName); } if(shiptypeid != null && !"".equals(shiptypeid)) { wheresql.append(" and n.shiptypeid=?"); olist.add(shiptypeid); request.setAttribute("shiptypeid", shiptypeid); } PageView<Box> pageView = new PageView<Box>(maxResult, page); qr = bs.getScrollData(pageView.getFirstResult(), pageView.getMaxresult(), wheresql.toString(), olist.toArray(), orderby); pageView.setQueryResult(qr); request.setAttribute("pageView", pageView); doBrowse(request, response, PageManage.addOtherPrefixAddress("boxList.jsp")); }?没错,我们采用了很像hibernate的where语句写法,完整的sql语句 :?
1=1 and?n.boxtype like ? and?n.shiptypeid=? ? ? ? 在olist加入参数的顺序必须和问号的顺序一致
底层包装后的显示?select n.* from box n where?1=1 and?n.boxtype like ? and?n.shiptypeid=??orderby boxid ASC
下面我们的考虑就是,如何将问号替换成参数,而且字符串和数字作为参数的形式还不一样,一个加' ' , 一个不加。
我们把这项职责还是交给DaoBase,代码如下:
private StringBuilder buildWhere(String whereSql, Object[] params) { StringBuilder where = new StringBuilder(); where.append(" and "); int temp = whereSql.lastIndexOf("?"); // 表达式中不含等号 if (temp == -1) { where.append(whereSql); } else { if (whereSql != null && params.length > 0) { String[] a = whereSql.split("[?]"); int para = a.length - 1; // "?"不是最后一个字符 if (temp < whereSql.length() - 1) { para = para - 1; } for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { where.append(a[i]); if (i <= para) { if (params[i] instanceof String || params[i] instanceof Timestamp || params[i] instanceof Date) { where.append("'").append(params[i]).append("'"); } else { where.append(params[i]); } } } } } return where; }?
相信大家应该明白了,这是怎么一回事儿了。 对于刚接触mybatis的朋友也没关系,我在此上传例子工程,供大家学习。由于个人精力有限,肯定多有设计不足之处,欢迎大家指正。