目录
wireless local area network(WLAN)
Vision Positioning System
Radar
wireless local area network(WLAN)
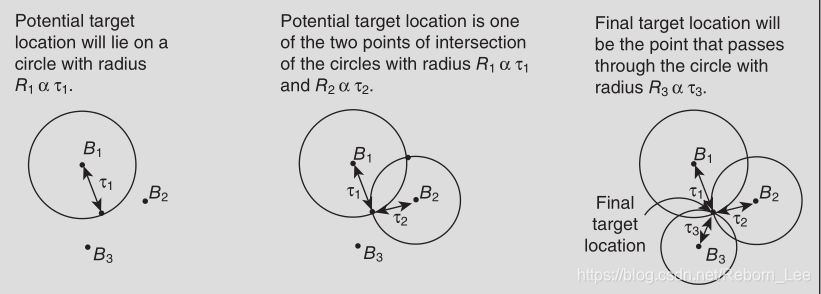
As the name suggests, WLAN is used for positioning and identification of objects in limited range. In this system, trilateration using the RSSI technique, shown in Figure 1.2 a, is used to localize the position of the object.
顾名思义,WLAN用于定位和识别有限范围内的物体。 在该系统中,使用RSSI技术进行三边测量,如图1.2a所示,用于定位对象的位置。
The strength of the signal that a wireless device or target object sends out is measured at multiple receivers to calculate the position . The WLAN positioning system consists of base stations and mobile hosts. Each base station and mobile host is equipped with a RF LAN technology - based digital network interface card ( NIC ) .
在多个接收器处测量无线设备或目标对象发出的信号的强度以计算位置。 WLAN定位系统由基站和移动主机组成。 每个基站和移动主机都配备了基于RF LAN技术的数字网络接口卡(NIC)[21]。
An algorithm is used to mitigate the interference due to noise and multipath. Mobile hosts periodically broadcast packets containing the start time and the transmitted signal strength information. Each base station records the start time, base station identifi cation, and transmitted signal strength. Using this start time, and the signal strength measurement at the base station, the location is determined by combining empirical measurements with signal propagation modeling. Similar to other systems such as GPS and AGPS, the clocks on the mobile hosts and the base stations need to be synchronized.
算法用于减轻由噪声和多径引起的干扰。 移动主机周期性地广播包含开始时间和发送信号强度信息的分组。 每个基站记录开始时间,基站标识和发送信号强度。 使用该开始时间和基站处的信号强度测量,通过将经验测量与信号传播建模相结合来确定位置。 与GPS和AGPS等其他系统类似,移动主机和基站上的时钟需要同步。
Vision Positioning System
In this positioning system, two cameras are used to localize the target object. As shown in Figure 1.4 c, these cameras [22] capture the picture of the target object. It can also be seen in the figure that the picture of the target object will be created at different locations relative to the center of the image.
在该定位系统中,使用两个摄像机来定位目标对象。 如图1.4c所示,这些摄像机[22]捕获目标对象的图像。 在图中还可以看出,目标对象的图片将在相对于图像中心的不同位置处创建。
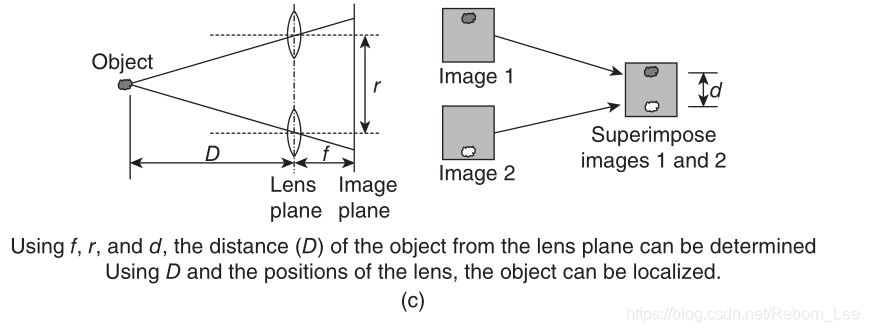
Superimposing these images, the disparity d in the locations of the object can be determined. Assuming that the distance r between the cameras and the focal length f of the cameras are known, the distance D of the object from the lens plane of the cameras can be calculated. Given known positions of two lenses and the calculated distance D , the target object can
be localized.
叠加这些图像,可以确定对象位置的视差d。 假设摄像机之间的距离r和摄像机的焦距f是已知的,可以计算物体距摄像机镜头平面的距离D. 给定两个透镜的已知位置和计算的距离D,可以定位目标对象。
Radar
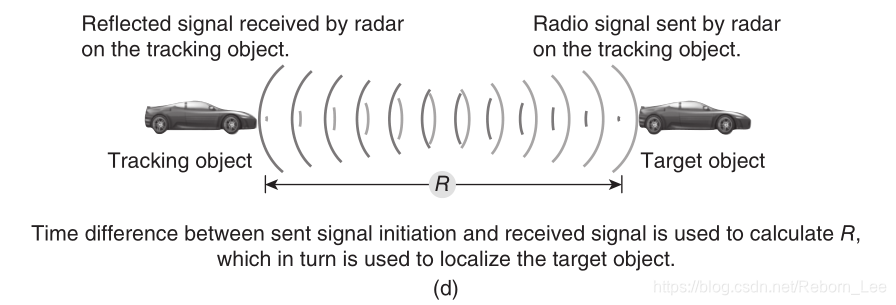
RADAR stands for radio detection and ranging. It is used to localize the position of a target in the surrounding areas by transmitting a short burst of energy and processing its reflection from the target [23] . Radar estimates the TOA of the refl ected signal and combines it with the DOA of the received signal measured by directional antennas.
RADAR代表无线电探测和测距。 它用于通过传输短脉冲能量并从目标处理其反射来定位周围区域中目标的位置[23]。 雷达估计反射信号的TOA,并将其与定向天线测量的接收信号的DOA相结合。
Let Δ t be the time between the transmitted signal and the received signal reflected from the target; the TOA is one - half of Δ t . Using the TOA, the distance of the object from the radar can be obtained (see Fig. 1.4 d). Assuming the position of the radar transmitter is known, the target can be localized using the calculated distance to the object.
令Δt为发射信号与从目标反射的接收信号之间的时间; TOA是Δt的一半。 使用TOA,可以获得物体与雷达的距离(见图1.4d)。 假设已知雷达发射器的位置,可以使用计算的到物体的距离来定位目标。