1st:An attempt at beating the 3D U-Net
德国癌症研究中心(DKFZ)医学图像计算部
Things new:Here we apply a 3D U-Net to the 2019 Kidney and Kidney Tumor Segmentation Challenge and attempt to improve upon it by augmenting it with residual and pre-activation residual blocks. And the residual 3D U-Net is chosen for test set prediction.
(将3D U-Net应用于KiTS19,并尝试通过增加残差和激活前残差block来对其进行改进,最后选择了残差3D U-net来做测试集预测。)
Model:

Preprocessing:
Resample to a common spacing of 3.22×1.62×1.62 mm resulting in median volume dimensions of 128 × 248 × 248 voxels. The CT intensities (HU) were clipped to a range of [-79, 304] and transformed by subtracting 101 and dividing by 76.9.
(将下载的KiTS19数据重新采样到3.22×1.62×1.62 mm的spacing,(之后协调靠考虑GPU等因素)中值体积尺寸为128×248×248体素。 将CT强度(HU)限制在[-79,304]范围内,并减去101再除以76.9,以进行变换。)
(其他的数据增强有:在train过程使用了batchgenerators框架。 另外在包括缩放,旋转,亮度,对比度,伽玛变换和高斯噪声的引入等方面做了调整。)
Things we learn:
要做spacing的原因以及spacing大小的选择;要做normalize的原因(另外这种独特的normalize的方法,我联想到了Andrew Ng在讲learning rate调整和feature scaling时提到的tips)
Results:
0.974 kidney Dice and a 0.851 tumor Dice resulting in a fifirst place 0.912 composite score.
Note:
除了主办方标记的问题case id 15和37之外,23,68,125和133在训练过程中发现异常而被排除;
文章基于nnUnet做了3D unet和剩余两种在此基础上的改变,但是发现这些对原始的3D Unet在这套数据集上以他们的调试参数和调试方法并没能带来显著的改善。因此,文章作者对这些类似的对于结构的改变所带来的改变需要进一步研究。
2nd:Cascaded Semantic Segmentation for Kidney and Tumor
上海平安科技
Things New:A triple -stage self-guided network for kidney tumor segmentation. Innovatively propose dilated convolution blocks (DCB) to replace the traditional pooling operations in deeper layers of U-Net architecture to retain detailed semantic information better. A hybrid loss of dice and weighted cross entropy is used to guide the model to focus on voxels close to the boundary and hard to be distinguished.
(采用三阶段自导网络完成肾脏肿瘤分割。 创新地提出了空洞卷积块(DCB),以取代U-Net体系结构更深层中的传统池化操作,以更好地保留详细的语义信息。 采用dice和加权交叉熵的混合损失来指导模型将注意力集中在边界附近且难以区分的体素上。)
Model:

Preprocessing:
Normalize all input images to zero mean and unit std (based on foreground voxels only). For the tumor refine network, image intensity values outside the kidney regions are set to zero, which can help remove the effect of background noise, as well as reducing the computational burden. The data augmentation methods include elastic deformation, rotation transform, gamma transformation, random cropping, etc
(将所有输入图像归一化为(0, 1)(仅针对前景体素)。 对于肿瘤细化网络,将肾脏区域外部的图像强度值设置为零,这可以帮助消除背景噪声的影响,并减轻计算负担。 数据扩充方法包括弹性变形,旋转变换,伽玛变换,随机裁剪等)
Things we learn:
We think pooling operations in deeper layers will blur the boundary of different classes and lose some detailed semantic information especially for small objects, such as tumors. Dilated convolution operations can retain details better and increase receptive field without increasing the size of parameters.
(我们认为,更深层的pooling操作将模糊不同类的边界,并丢失一些详细的语义信息,尤其是对于诸如肿瘤之类的小物体。 空洞卷积运算可以更好地保留细节,并在不增加参数大小的情况下增加FOV。)
emmm,我印象中空洞卷积在做那稍大型结构的分割时效果会好很多。但是将空洞卷积放在深层layer里面替换pooling,,我的理解是,在最终调好参数的情况下,随layer层数增加,在等到换用空洞卷积的时候,网络已经foucs在一个适当大小的视野(即可以合适地纵览整个肾脏和肿瘤部分)了,这个时候空洞卷积或者真的可以有良好的效果。
Results:
0.9674, 0.8454 average dice for kidney and tumor respectively
Note:
针对常见的class imbalance,文章自己创新了一种Loss,在stage 2和stage 3里面用,具体如下:
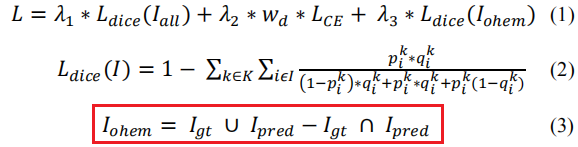
这里相当于加大了对假阳和假阴的惩罚,所以应当是有可取之处的。并且文章里面做了实验验证,证明了他的结构性创新和新的损失函数设置以及整体流程的合理性,详见文章:

3rd:Segmentation of kidney tumor by multi-resolution VB-nets
上海联影;南方医科大学;北大第一医院
Things new:We adopt two resolutions and propose a customized V-Net model called VB-Net for both resolutions. The VB-Net model in the coarse resolution can robustly localize the organs, while the VB-Net model in the fine resolution can accurately refine the boundary of each organ or lesion.
(我们采用两种分辨率,并针对这两种分辨率提出了一个称为VB-Net的定制V-Net模型。 粗分辨率的VB-Net模型可以稳健地定位器官,而高分辨率的VB-Net模型可以准确地细化每个器官或病变的边界。)
Model:

讲道理,这幅图真的敷衍。。
Our VB-Net replaces the conventional convolutional layers inside V-Net with the bottleneck structure. Due to the use of bottle-neck structure, we named the architecture as VB-Net (B stands for bottle-neck). The bottleneck structure consists of three convolutional layers. The first convolutional layer applies a 1×1×1 convolutional kernel to reduce the channels of feature maps. The second convolutional layer performs a spatial convolution with the same kernel size as the conventional convolutional layer. The last convolutional layer applies a 1×1×1 convolution kernel to increase the channels of feature maps back to the original size.
(我们的VB-Net用瓶颈结构代替了V-Net中的常规卷积层。 由于使用了瓶颈结构,我们将该架构命名为VB-Net(B代表瓶颈)。 瓶颈结构由三个卷积层组成。 第一卷积层应用1×1×1卷积核以减少特征图的通道。 第二卷积层执行与传统卷积层相同的内核大小的空间卷积。 最后的卷积层应用1×1×1卷积核,以将特征图的通道增加回原始大小。)
以此变化,模型的参数量急剧减小(250M V-net to 8.8M VB-net);速度加快。(文章中提到这个size的model可以考虑部署到云或者是移动app上,产品应用化的思考,值得借鉴)
Preprocessing:
Truncate the image intensity values of all images to the range of [-200, 500] HU to remove the irrelevant details. Then, truncated intensity values are normalized into the range of [-1, 1].
(将所有图像的图像强度值截断为[-200,500] HU范围,以删除无关的细节。 然后,将截断的强度值归一化为[-1,1]的范围。)
Resample images into the same isotropic resolution. In the coarse resolution (resampled to 6 mm), we train a VB-Net to roughly localize the volume of interest (VOI) for the whole kidney. In the fine resolution (resampled to 1 mm), we train VB-Net to accurately delineate the kidney and tumor boundary within the detected VOI.
(将图像重新采样为相同的各向同性分辨率。在粗略分辨率(重采样到6mm)中,我们训练了VB-Net来大致定位整个肾脏的目标体积(VOI)。 在高分辨率(重采样到1mm)中,我们训练VB-Net来准确描绘检测到的VOI内的肾脏和肿瘤边界。)
Postprocessing:
To improve performance further, we remove the isolated small segments out of kidney by picking the largest connected component.
Things we learn:
V-Net encourages much smoother gradient flow, thus easier in optimization and convergence.
Images in the training set have 512×512 pixels in-plane size with spatial resolution varying from 0.438 mm to 1.04 mm, and the number of slices varies from 29 to 1059 with a slice thickness between 0.5 mm and 5 mm.
Results:

Note:
专业医生手动注释了肾囊肿作为附加类别,以改善囊肿和肿瘤之间的分类,实验中证明可以有效增强模型的区分能力,但是对于密度不均匀的囊肿或者肿瘤,模型效果不佳,对此,作者使用了后处理算法,其主要依据囊肿和肿瘤之间的空间关系及其平均HU对误差区域进行校正(无详细说明)。
4th:Cascaded Volumetric Convolutional Network for Kidney Tumor Segmentation from CT volumes
中国科学院;中国科学院大学;东南大学;联想研究院AI实验室
Things new:a two-stage framework for kidney and tumor segmentation based on 3D fully convolutional network (FCN). The first stage preliminarily locate the kidney and cut off the irrelevant background to reduce class imbalance and computation cost. Then the second stage precisely segment the kidney and tumor on the cropped patch.
(基于3D全卷积网络(FCN)的肾脏和肿瘤分割的两阶段框架。 第一阶段初步定位肾脏并切除无关的背景,以减少class imbalance和计算成本。 然后,第二阶段将肾脏和肿瘤精确地切成patch。)
Model:


Preprocessing:
Resampling:stage1: downsample the 2D planes of the original images along the slice axis, which has the lowest resolution, by doubling the slice axis voxel spacing. That will compatibilize resolutions along three dimensions so that the anisotropy problem can be ameliorated.
(通过将切片轴体素间距加倍,可以沿切片轴对原始图像的2D平面进行降采样。 这将使三个方向的分辨率兼容,从而可以改善各向异性问题。)
Normalization:for each data case, 1) do percentile clipping of (0.05%, 99.5%) to remove outliers and 2) do standardization by subtracting the mean and standard deviation values collected in statistics collecting step.
(对于每个数据案例,1)对(0.05%,99.5%)进行百分位数裁剪,以消除异常值; 2)通过减去在统计信息收集步骤中收集的平均值和标准偏差值进行标准化。)
Postprocessing:
A connected component analysis to remove false positives.
Results:
