Android系统在启动SystemServer进程时,通过两个阶段来启动系统所有服务,在第一阶段启动本地服务,如SurfaceFlinger,SensorService等,在第二阶段则启动一系列的Java服务。开机动画是在什么时候启动的呢?通过查看源码,Android开机动画是在启动SurfaceFlinger服务时启动的。SystemServer的main函数首先调用init1来启动本地服务,init1函数通过JNI调用C语言中的system_init()函数来实现服务启动。
extern "C" status_t system_init(){ sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self()); sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager(); sp<GrimReaper> grim = new GrimReaper(); sm->asBinder()->linkToDeath(grim, grim.get(), 0); char propBuf[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX]; property_get("system_init.startsurfaceflinger", propBuf, "1"); if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) { // Start the SurfaceFlinger SurfaceFlinger::instantiate(); } ... return NO_ERROR;}通过调用SurfaceFlinger::instantiate()函数来启动SurfaceFlinger服务,SurfaceFlinger类继承于BinderService模板类,BinderService类的instantiate()函数就是构造对应类型的服务对象,并注册到ServiceManager进程中。static void instantiate() { publish(); }static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false) { sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager()); return sm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()), new SERVICE(), allowIsolated);}对于SurfaceFlinger服务来说,就是首先构造SurfaceFlinger对象,然后通过调用ServiceManger的远程Binder代理对象的addService函数来注册SurfaceFlinger服务。这里只介绍SurfaceFlinger的构造过程,对于服务注册过程,在Android服务注册完整过程源码分析中已经介绍的非常详细。
SurfaceFlinger::SurfaceFlinger() : BnSurfaceComposer(), Thread(false), mTransactionFlags(0), mTransationPending(false), mLayersRemoved(false), mBootTime(systemTime()), mVisibleRegionsDirty(false), mHwWorkListDirty(false), mElectronBeamAnimationMode(0), mDebugRegion(0), mDebugDDMS(0), mDebugDisableHWC(0), mDebugDisableTransformHint(0), mDebugInSwapBuffers(0), mLastSwapBufferTime(0), mDebugInTransaction(0), mLastTransactionTime(0), mBootFinished(false), mSecureFrameBuffer(0){ init();}SurfaceFlinger对象实例的构造过程很简单,就是初始化一些成员变量值,然后调用init()函数来完成初始化工作void SurfaceFlinger::init(){ char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX]; property_get("debug.sf.showupdates", value, "0"); mDebugRegion = atoi(value);#ifdef DDMS_DEBUGGING property_get("debug.sf.ddms", value, "0"); mDebugDDMS = atoi(value); if (mDebugDDMS) { DdmConnection::start(getServiceName()); }#endif property_get("ro.bootmode", value, "mode"); if (!(strcmp(value, "engtest") && strcmp(value, "special") && strcmp(value, "wdgreboot") && strcmp(value, "unknowreboot") && strcmp(value, "panic"))) { SurfaceFlinger::sBootanimEnable = false; }}在SurfaceFlinger的init函数中,也并没有做任何复杂工作,只是简单读取系统属性得到开机模式,来相应设置一些变量而已,比如是否显示开机动画变量sBootanimEnable。由于SurfaceFlinger继承于RefBase类,并重写了该类的onFirstRef()函数,我们知道,RefBase类的子类对象在第一次创建时,会自动调用onFirstRef()函数,因此在SurfaceFlinger对象构造完成时,将调用onFirstRef()函数。void SurfaceFlinger::onFirstRef(){ mEventQueue.init(this);//事件队列初始化 run("SurfaceFlinger", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);//运行SurfaceFlinger线程 mReadyToRunBarrier.wait();}这里不对SurfaceFlinger的相关内容做详细介绍,本文的主要内容是介绍开机动画显示过程。由于SurfaceFlinger同时继承于线程Thread类,而且SurfaceFlinger并没有重写Thread类的run方法,因此这里调用SurfaceFlinger的run函数,其实调用的就是其父类Thread的run函数。status_t Thread::run(const char* name, int32_t priority, size_t stack){ Mutex::Autolock _l(mLock); if (mRunning) { return INVALID_OPERATION; } mStatus = NO_ERROR; mExitPending = false; mThread = thread_id_t(-1); mHoldSelf = this; mRunning = true; bool res; if (mCanCallJava) { res = createThreadEtc(_threadLoop,this, name, priority, stack, &mThread); } else { res = androidCreateRawThreadEtc(_threadLoop,this, name, priority, stack, &mThread); } if (res == false) { mStatus = UNKNOWN_ERROR; // something happened! mRunning = false; mThread = thread_id_t(-1); mHoldSelf.clear(); // "this" may have gone away after this. return UNKNOWN_ERROR; } return NO_ERROR;}该函数就是创建一个线程,并运行现在执行函数_threadLoop
int Thread::_threadLoop(void* user){ Thread* const self = static_cast<Thread*>(user); sp<Thread> strong(self->mHoldSelf); wp<Thread> weak(strong); self->mHoldSelf.clear();#ifdef HAVE_ANDROID_OS self->mTid = gettid();#endif bool first = true; do { bool result; if (first) { first = false; self->mStatus = self->readyToRun(); result = (self->mStatus == NO_ERROR); if (result && !self->exitPending()) { result = self->threadLoop(); } } else { result = self->threadLoop(); } { Mutex::Autolock _l(self->mLock); if (result == false || self->mExitPending) { self->mExitPending = true; self->mRunning = false; self->mThread = thread_id_t(-1); self->mThreadExitedCondition.broadcast(); break; } } strong.clear(); strong = weak.promote(); } while(strong != 0); return 0;}在线程开始运行时,变量first为true,因此会调用self->readyToRun()来做一些初始化工作,同时将变量first设置为false,在以后线程执行过程中,就反复执行self->threadLoop()了。作为Thread类的子类SurfaceFlinger重写了这两个方法,因此创建的SurfaceFlinger线程在执行前会调用SurfaceFlinger的readyToRun()函数完成初始化任务,然后反复执行SurfaceFlinger的threadLoop()函数。status_t SurfaceFlinger::readyToRun(){ ALOGI( "SurfaceFlinger's main thread ready to run. " "Initializing graphics H/W..."); int dpy = 0; { // initialize the main display GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy)); DisplayHardware* const hw = new DisplayHardware(this, dpy); plane.setDisplayHardware(hw); } // create the shared control-block mServerHeap = new MemoryHeapBase(4096,MemoryHeapBase::READ_ONLY, "SurfaceFlinger read-only heap"); ALOGE_IF(mServerHeap==0, "can't create shared memory dealer"); mServerCblk = static_cast<surface_flinger_cblk_t*>(mServerHeap->getBase()); ALOGE_IF(mServerCblk==0, "can't get to shared control block's address"); new(mServerCblk) surface_flinger_cblk_t; // initialize primary screen const GraphicPlane& plane(graphicPlane(dpy)); const DisplayHardware& hw = plane.displayHardware(); const uint32_t w = hw.getWidth(); const uint32_t h = hw.getHeight(); const uint32_t f = hw.getFormat(); hw.makeCurrent(); // initialize the shared control block mServerCblk->connected |= 1<<dpy; display_cblk_t* dcblk = mServerCblk->displays + dpy; memset(dcblk, 0, sizeof(display_cblk_t)); dcblk->w = plane.getWidth(); dcblk->h = plane.getHeight(); dcblk->format = f; dcblk->orientation = ISurfaceComposer::eOrientationDefault; dcblk->xdpi = hw.getDpiX(); dcblk->ydpi = hw.getDpiY(); dcblk->fps = hw.getRefreshRate(); dcblk->density = hw.getDensity(); // Initialize OpenGL|ES glPixelStorei(GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT, 4); glPixelStorei(GL_PACK_ALIGNMENT, 4); glEnableClientState(GL_VERTEX_ARRAY); glShadeModel(GL_FLAT); glDisable(GL_DITHER); glDisable(GL_CULL_FACE); const uint16_t g0 = pack565(0x0F,0x1F,0x0F); const uint16_t g1 = pack565(0x17,0x2f,0x17); const uint16_t wormholeTexData[4] = { g0, g1, g1, g0 }; glGenTextures(1, &mWormholeTexName); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mWormholeTexName); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT); glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, 2, 2, 0,GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5, wormholeTexData); const uint16_t protTexData[] = { pack565(0x03, 0x03, 0x03) }; glGenTextures(1, &mProtectedTexName); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mProtectedTexName); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT); glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, 1, 1, 0,GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5, protTexData); glViewport(0, 0, w, h); glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION); glLoadIdentity(); // put the origin in the left-bottom corner glOrthof(0, w, 0, h, 0, 1); // l=0, r=w ; b=0, t=h // start the EventThread mEventThread = new EventThread(this); mEventQueue.setEventThread(mEventThread); hw.startSleepManagement(); /* * We're now ready to accept clients... */ mReadyToRunBarrier.open(); // start boot animation startBootAnim(); return NO_ERROR;}该函数首先是初始化Android的图形显示系统,启动SurfaceFlinger事件线程,这些内容只有了解了Android的显示原理及SurfaceFlinger服务之后才能理解,这里不做介绍。当显示系统初始化完毕后,调用startBootAnim()函数来显示开机动画。void SurfaceFlinger::startBootAnim() { // start boot animation if(SurfaceFlinger::sBootanimEnable){ property_set("service.bootanim.exit", "0"); property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim"); }}startBootAnim()函数比较简单,就是通过判断开机动画的变量值了决定是否显示开机动画。启动开机动画进程也是通过Android属性系统来实现的,具体启动过程可以查看Android 系统属性SystemProperty分析。在Android系统启动脚本init.rc中配置了开机动画服务进程。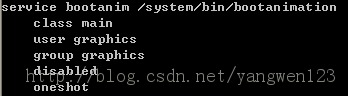
property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim")就是启动bootanim进程来显示开机动画,该进程对应的源码位于frameworks\base\cmds\bootanimation\bootanimation_main.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv){#if defined(HAVE_PTHREADS) setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, ANDROID_PRIORITY_DISPLAY);#endif char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX]; property_get("debug.sf.nobootanimation", value, "0"); int noBootAnimation = atoi(value); ALOGI_IF(noBootAnimation, "boot animation disabled"); if (!noBootAnimation) { /*modify boot animation and added shutdown animation*/ char argvtmp[2][BOOTANIMATION_PATHSET_MAX]; memset(argvtmp[0],0,BOOTANIMATION_PATHSET_MAX); memset(argvtmp[1],0,BOOTANIMATION_PATHSET_MAX); //没有参数时,执行开机动画, if(argc<2){ //开机动画文件BOOTANIMATION_BOOT_FILM_PATH_DEFAULT="/system/media/bootanimation.zip" strncpy(argvtmp[0],BOOTANIMATION_BOOT_FILM_PATH_DEFAULT,BOOTANIMATION_PATHSET_MAX); //开机声音文件BOOTANIMATION_BOOT_SOUND_PATH_DEFAULT="/system/media/bootsound.mp3" strncpy(argvtmp[1],BOOTANIMATION_BOOT_SOUND_PATH_DEFAULT,BOOTANIMATION_PATHSET_MAX); }else{//否则执行关机动画 //关机动画文件BOOTANIMATION_SHUTDOWN_FILM_PATH_DEFAULT="/system/media/shutdownanimation.zip" strncpy(argvtmp[0],BOOTANIMATION_SHUTDOWN_FILM_PATH_DEFAULT,BOOTANIMATION_PATHSET_MAX); //关机声音文件BOOTANIMATION_SHUTDOWN_SOUND_PATH_DEFAULT="/system/media/shutdownsound.mp3" strncpy(argvtmp[1],BOOTANIMATION_SHUTDOWN_SOUND_PATH_DEFAULT,BOOTANIMATION_PATHSET_MAX); } __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,"BootAnimation", "begine bootanimation!"); //启动Binder线程池,用于接收其他进程的请求 sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self()); ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool(); //创建BootAnimation对象 BootAnimation *boota = new BootAnimation(); String8 descname("desc.txt"); if(argc<2){//设置开机动画文件的默认路径 String8 mpath_default(BOOTANIMATION_BOOT_FILM_PATH_DEFAULT); String8 spath_default(BOOTANIMATION_BOOT_SOUND_PATH_DEFAULT); boota->setmoviepath_default(mpath_default); boota->setsoundpath_default(spath_default); //boota->setdescname_default(descname_default); }else {//设置关机动画文件的默认路径 String8 mpath_default(BOOTANIMATION_SHUTDOWN_FILM_PATH_DEFAULT); String8 spath_default(BOOTANIMATION_SHUTDOWN_SOUND_PATH_DEFAULT); boota->setmoviepath_default(mpath_default); boota->setsoundpath_default(spath_default); //boota->setdescname_default(descname_default); __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,"BootAnimation","shutdown exe bootanimation!"); } String8 mpath(argvtmp[0]); String8 spath(argvtmp[1]); //设置动画的文件路径 boota->setmoviepath(mpath); boota->setsoundpath(spath); boota->setdescname(descname); __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,"BootAnimation","%s", mpath.string()); __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,"BootAnimation","%s", spath.string()); sp<BootAnimation> bootsp = boota; //将当前线程注册到Binder线程池中 IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool(); } return 0;}该函数构造了一个BootAnimation对象,并且为该对象设置了开关机动画及声音文件路径,同时创建了Binder线程池,并将bootanim进程的主线程注册到Binder线程池中,用于接收客户进程的Binder通信请求。
BootAnimation::BootAnimation() : Thread(false){ mSession = new SurfaceComposerClient();}在构造BootAnimation对象时,实例化SurfaceComposerClient对象,用于请求SurfaceFlinger显示开关机动画。由于BootAnimation类继承于RefBase,同时重写了onFirstRef()函数,因此在构造BootAnimation对象时,会调用该函数。void BootAnimation::onFirstRef() { status_t err = mSession->linkToComposerDeath(this); ALOGE_IF(err, "linkToComposerDeath failed (%s) ", strerror(-err)); if (err == NO_ERROR) { run("BootAnimation", PRIORITY_DISPLAY); }}该函数首先为SurfaceComposerClient对象注册Binder死亡通知,然后调用BootAnimation的run方法,由于BootAnimation同时继承于Thread类,前面介绍SurfaceFlinger时已经介绍到,当某个类继承于Thread类时,当调用该类的run函数时,函数首先会执行readyToRun()函数来完成线程执行前的一些工作,然后线程反复执行threadLoop()函数,在BootAnimation类中,同样重新了这两个方法status_t BootAnimation::readyToRun() { //force screen display in vertical layout mSession->setOrientation(0, 0, 0); mAssets.addDefaultAssets(); DisplayInfo dinfo; status_t status = session()->getDisplayInfo(0, &dinfo); if (status) return -1; // create the native surface sp<SurfaceControl> control; if (dinfo.w > dinfo.h) { control = session()->createSurface(0, dinfo.h, dinfo.w, PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565); } else { control = session()->createSurface(0, dinfo.w, dinfo.h, PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565); } SurfaceComposerClient::openGlobalTransaction(); control->setLayer(0x40000000); SurfaceComposerClient::closeGlobalTransaction(); sp<Surface> s = control->getSurface(); // initialize opengl and egl const EGLint attribs[] = { EGL_RED_SIZE, 8, EGL_GREEN_SIZE, 8, EGL_BLUE_SIZE, 8, EGL_DEPTH_SIZE, 0, EGL_NONE }; EGLint w, h, dummy; EGLint numConfigs; EGLConfig config; EGLSurface surface; EGLContext context; EGLDisplay display = eglGetDisplay(EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY); eglInitialize(display, 0, 0); eglChooseConfig(display, attribs, &config, 1, &numConfigs); surface = eglCreateWindowSurface(display, config, s.get(), NULL); context = eglCreateContext(display, config, NULL, NULL); eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_WIDTH, &w); eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_HEIGHT, &h); if (eglMakeCurrent(display, surface, surface, context) == EGL_FALSE) return NO_INIT; mDisplay = display; mContext = context; mSurface = surface; mWidth = w; mHeight = h; mFlingerSurfaceControl = control; mFlingerSurface = s; mAndroidAnimation = true; // If the device has encryption turned on or is in process // of being encrypted we show the encrypted boot animation. char decrypt[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX]; property_get("vold.decrypt", decrypt, ""); bool encryptedAnimation = atoi(decrypt) != 0 || !strcmp("trigger_restart_min_framework", decrypt); //如果"/system/media/bootanimation-encrypted.zip"文件存在或者设置的动画文件存在,或者默认动画文件存在,或者"/data/local/bootanimation.zip"文件存在,都显示开机动画文件,否则显示Android滚动字样 if ((encryptedAnimation && (access(SYSTEM_ENCRYPTED_BOOTANIMATION_FILE, R_OK) == 0) && (mZip.open(SYSTEM_ENCRYPTED_BOOTANIMATION_FILE) == NO_ERROR)) || ((access(moviepath, R_OK) == 0) && (mZip.open(moviepath) == NO_ERROR)) || ((access(movie_default_path, R_OK) == 0) && (mZip.open(movie_default_path) == NO_ERROR)) || ((access(USER_BOOTANIMATION_FILE, R_OK) == 0) && (mZip.open(USER_BOOTANIMATION_FILE) == NO_ERROR))) { mAndroidAnimation = false; } return NO_ERROR;}在该函数里创建SurfaceControl对象,通过SurfaceControl对象得到Surface对象,并初始化好OpenGL,同时判断动画文件是否存在,如果不存在,则设置标志位mAndroidAnimation为true,表示显示Android滚动字样。当初始化完这些必需资源后,线程进入循环执行体threadLoop()bool BootAnimation::threadLoop(){ bool r; //如果mAndroidAnimation为true,表示动画文件不存在,则显示Android滚动字样 if (mAndroidAnimation) { r = android(); } else {//显示动画 r = movie(); } //资源回收 eglMakeCurrent(mDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT); eglDestroyContext(mDisplay, mContext); eglDestroySurface(mDisplay, mSurface); mFlingerSurface.clear(); mFlingerSurfaceControl.clear(); eglTerminate(mDisplay); IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess(); return r;}开机画面主要是由一个zip格式的压缩包bootanimation.zip组成,压缩包里面包含数张png格式的图片,还有一个desc.txt的文本文档,开机时按desc.txt里面的指令,屏幕上会按文件名称顺序连续的播放一张张的图片,就像播放原始的胶带影片一样,形成动画。desc.txt是一个保存形式为ANSI格式的文件,用于设置这个动画像素(大小),帧数,闪烁次数,文件夹名称等。内容如下:480 854 10
p 1 2 folder1
p 0 2 folder2
480 427 30 ---这里的480代表图片的像素(大小)宽度,427代表图片的像素(大小)高度,30代表帧数;
p 1 0 part0 ---这里的p代表标志符,1代表循环次数为1次,0代表阶段间隔时间为0,part0代表对应的文件夹名,为第一阶段动画图片目录;
p 0 0 part1---这里的p代表标志符,0代表本阶段无限循环,0代表阶段间隔时间为0,part1代表对应的文件夹名,为第二阶段动画图片目录;
阶段切换间隔时间:单位是一个帧的持续时间,比如帧数是30,那么帧的持续时间就是1秒/30 = 33.3毫秒。阶段切换间隔时间期间开机动画进程进入休眠,把CPU时间让给初始化系统使用。也就是间隔长启动会快,但会影响动画效果。
folder1和folder2文件夹内包含的是两个动画的系列图片,图片为PNG格式。

bool BootAnimation::movie(){ ZipFileRO& zip(mZip); //获取zip压缩文件中的文件数目 size_t numEntries = zip.getNumEntries(); //打开zip压缩文件中的desc.txt文件 ZipEntryRO desc = zip.findEntryByName("desc.txt"); FileMap* descMap = zip.createEntryFileMap(desc); ALOGE_IF(!descMap, "descMap is null"); if (!descMap) { return false; } //读取desc.txt文件内容 String8 desString((char const*)descMap->getDataPtr(),descMap->getDataLength()); char const* s = desString.string(); Animation animation; //读取persist.sys.silence属性来决定是否播放开机音乐 char silence[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX]; property_get("persist.sys.silence", silence, "0"); if(strcmp("1", silence)==0){ // do something. }else{ soundplay(); } //解析desc.txt文件内容 for (;;) { //从字符串s中查找是否有字符串"\n",如果有,返回s中"\n"起始位置的指针,如果没有,返回null。 const char* endl = strstr(s, "\n"); if (!endl) break; //取得文件一行内容 String8 line(s, endl - s); const char* l = line.string(); int fps, width, height, count, pause; char path[256]; char pathType; //从文件第一行中读取宽度,高度,帧数 //480 854 10 <---> width height fps if (sscanf(l, "%d %d %d", &width, &height, &fps) == 3) { //LOGD("> w=%d, h=%d, fps=%d", fps, width, height); animation.width = (width > 0 ? width : mWidth); animation.height = (height > 0 ? height : mHeight); animation.fps = fps; //p 1 2 folder1 <---> pathType count pause path }else if (sscanf(l, " %c %d %d %s", &pathType, &count, &pause, path) == 4) { //LOGD("> type=%c, count=%d, pause=%d, path=%s", pathType, count, pause, path); Animation::Part part;//一个part描述一个动画文件夹内容 part.playUntilComplete = pathType == 'c'; part.count = count; part.pause = pause; part.path = path; animation.parts.add(part); } s = ++endl; } //读取动画个数 const size_t pcount = animation.parts.size(); //遍历zip压缩包中的所有文件 for (size_t i=0 ; i<numEntries ; i++) { char name[256]; ZipEntryRO entry = zip.findEntryByIndex(i); //读取压缩包中的文件名称,所在目录的路径 if (zip.getEntryFileName(entry, name, 256) == 0) { const String8 entryName(name); const String8 path(entryName.getPathDir()); const String8 leaf(entryName.getPathLeaf()); if (leaf.size() > 0) { for (int j=0 ; j<pcount ; j++) { if (path == animation.parts[j].path) { int method; //获取文件信息 if (zip.getEntryInfo(entry, &method, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)) { if (method == ZipFileRO::kCompressStored) { FileMap* map = zip.createEntryFileMap(entry); if (map) { Animation::Frame frame; frame.name = leaf; frame.map = map; Animation::Part& part(animation.parts.editItemAt(j)); part.frames.add(frame); } } } } } } } } // clear screen glShadeModel(GL_FLAT); glDisable(GL_DITHER); glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST); glDisable(GL_BLEND); glClearColor(0,0,0,1); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0); glEnable(GL_TEXTURE_2D); glTexEnvx(GL_TEXTURE_ENV, GL_TEXTURE_ENV_MODE, GL_REPLACE); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); const int xc = (mWidth - animation.width) / 2; const int yc = ((mHeight - animation.height) / 2); nsecs_t lastFrame = systemTime(); nsecs_t frameDuration = s2ns(1) / animation.fps; Region clearReg(Rect(mWidth, mHeight)); clearReg.subtractSelf(Rect(xc, yc, xc+animation.width, yc+animation.height)); for (int i=0 ; i<pcount ; i++) { const Animation::Part& part(animation.parts[i]); const size_t fcount = part.frames.size(); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0); for (int r=0 ; !part.count || r<part.count ; r++) { // Exit any non playuntil complete parts immediately if(exitPending() && !part.playUntilComplete) break; for (int j=0 ; j<fcount && (!exitPending() || part.playUntilComplete) ; j++) { const Animation::Frame& frame(part.frames[j]); nsecs_t lastFrame = systemTime(); if (r > 0) { glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, frame.tid); } else { if (part.count != 1) { glGenTextures(1, &frame.tid); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, frame.tid); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); } initTexture( frame.map->getDataPtr(), frame.map->getDataLength()); } if (!clearReg.isEmpty()) { Region::const_iterator head(clearReg.begin()); Region::const_iterator tail(clearReg.end()); glEnable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST); while (head != tail) { const Rect& r(*head++); glScissor(r.left, mHeight - r.bottom, r.width(), r.height()); glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); } glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST); } glDrawTexiOES(xc, yc, 0, animation.width, animation.height); eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface); nsecs_t now = systemTime(); nsecs_t delay = frameDuration - (now - lastFrame); //ALOGD("%lld, %lld", ns2ms(now - lastFrame), ns2ms(delay)); lastFrame = now; if (delay > 0) { struct timespec spec; spec.tv_sec = (now + delay) / 1000000000; spec.tv_nsec = (now + delay) % 1000000000; int err; do { err = clock_nanosleep(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, TIMER_ABSTIME, &spec, NULL); } while (err<0 && errno == EINTR); } checkExit(); } usleep(part.pause * ns2us(frameDuration)); // For infinite parts, we've now played them at least once, so perhaps exit if(exitPending() && !part.count) break; } // free the textures for this part if (part.count != 1) { for (int j=0 ; j<fcount ; j++) { const Animation::Frame& frame(part.frames[j]); glDeleteTextures(1, &frame.tid); } } } soundstop(); return false;}