其实,有很多方法可以实现一个Layout的抽屉拉伸效果,最经常的方法就是自定义一个ViewGroup,然后控制点击事件,控制移动之类的,这种方法的代码量多,而且实现起来复杂,后期维护增加其他效果也很麻烦,直到今天看到了 ViewDragHelper这个类,就是专门为实现View的移动而生的,我就试着开发了一个抽屉拉伸的效果,效果图如下:
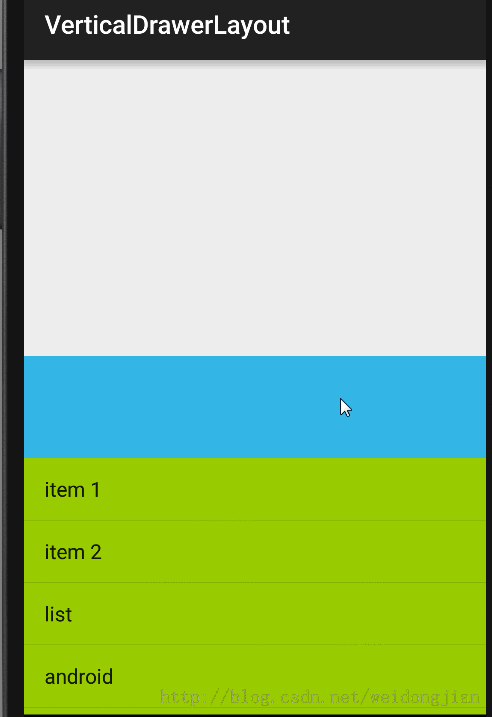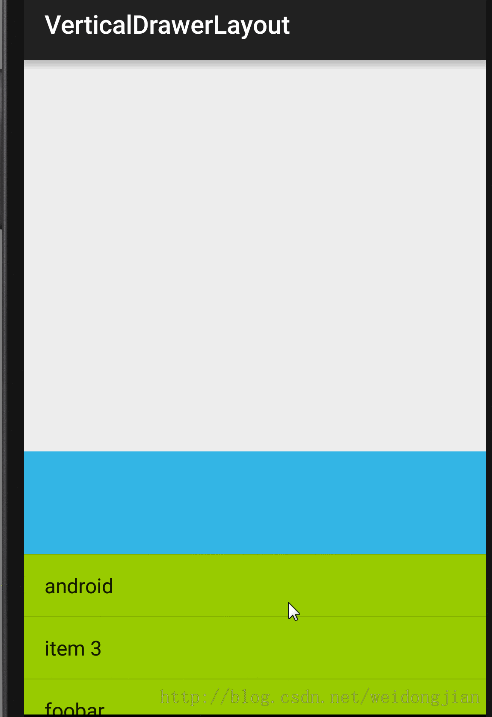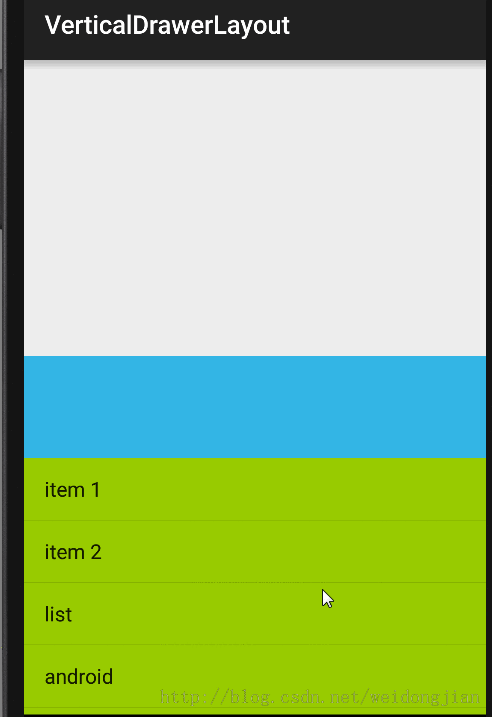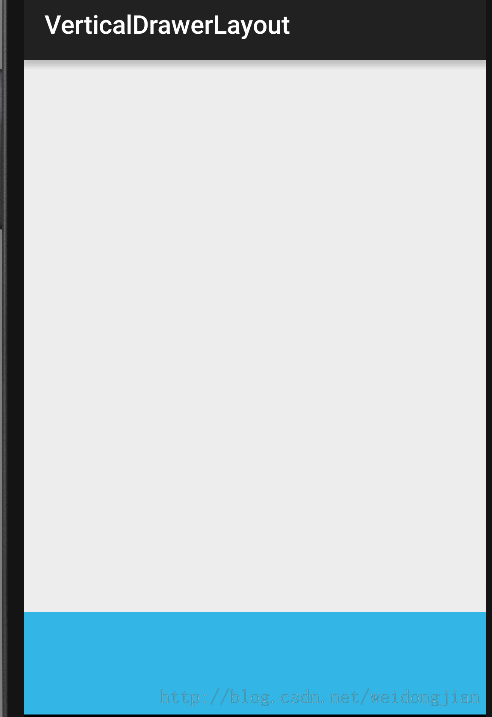
所有移动的控制在ViewDragHelper.Callback里面来实现,移动就用dragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo来实现,而且Callback集成了许多的方法,方便后期的维护或者增加其他功能。
首先看下最核心的DragLayout的代码
public class DragLayout extends LinearLayout { private ViewDragHelper dragHelper; private View mDragView, contentView; private int dragRange; public DragLayout(Context context) { super(context); init(); } public DragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); init(); } @TargetApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) public DragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes); init(); } public DragLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); init(); } private void init() { dragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, callback); } @Override protected void onFinishInflate() { super.onFinishInflate(); mDragView = findViewById(R.id.dragView); contentView = findViewById(R.id.contentView); } private ViewDragHelper.Callback callback = new ViewDragHelper.Callback() { @Override public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) { return child == mDragView; } @Override public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) { contentView.layout(0, top + mDragView.getHeight(), getWidth(), top + mDragView.getHeight() + dragRange); } @Override public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) { int topBound = getHeight() - dragRange - mDragView.getHeight(); int bottomBound = getHeight() - mDragView.getHeight(); final int newHeight = Math.min(Math.max(topBound, top), bottomBound); return newHeight; } @Override public int getViewVerticalDragRange(View child) { return dragRange; } @Override public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) { super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel); if (yvel > 0) { smoothToBottom(); }else if (yvel < 0) { smoothToTop(); } } }; @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); dragRange = contentView.getMeasuredHeight(); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); mDragView.layout(0, getHeight() - mDragView.getHeight(), getWidth(), getHeight()); contentView.layout(0, getHeight(), getWidth(), getHeight() + dragRange); } @Override public boolean onInterceptHoverEvent(MotionEvent event) { final int action = MotionEventCompat.getActionMasked(event); if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL || action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP) { dragHelper.cancel(); return false; } return dragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(event); } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { dragHelper.processTouchEvent(event); return true; } private void smoothToTop() { if (dragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mDragView, getPaddingLeft(), getHeight() - dragRange - mDragView.getHeight())) { ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this); } } private void smoothToBottom() { if (dragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mDragView, getPaddingLeft(), getHeight() - mDragView.getHeight())) { ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this); } } @Override public void computeScroll() { if (dragHelper.continueSettling(true)) { ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this); } }}在这里面,初始化了ViewDragHelper
dragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, callback);
设置垂直方向的移动距离,这里设置为listview的高度:
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
int topBound = getHeight() - dragRange - mDragView.getHeight();
int bottomBound = getHeight() - mDragView.getHeight();
final int newHeight = Math.min(Math.max(topBound, top), bottomBound);
return newHeight;
}
监听位置的移动,移动listview,让他始终挨在DrawView的下面:
@Overridepublic void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView, int left, int top, int dx, int dy) { contentView.layout(0, top + mDragView.getHeight(), getWidth(), top + mDragView.getHeight() + dragRange);}
在OnLayout里面重新布局,隐藏listView:
@Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { super.onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); mDragView.layout(0, getHeight() - mDragView.getHeight(), getWidth(), getHeight()); contentView.layout(0, getHeight(), getWidth(), getHeight() + dragRange); }接下来是XML的布局:
<cn.xm.weidongjian.verticaldrawerlayout.DragLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <View android:id="@+id/dragView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="80dp" android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_light"/> <ListView android:scrollbars="none" android:id="@+id/contentView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="200dp" android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"/></cn.xm.weidongjian.verticaldrawerlayout.DragLayout>
很简单,自定义的View里面放置两个View
最后的MainActivity:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { String[] listItems = {"item 1", "item 2 ", "list", "android", "item 3", "foobar", "bar", }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ListView listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.contentView); listView.setAdapter(new ArrayAdapter(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, listItems)); }}最后,这个Demo只是实现一个很简单的功能,不过大概可以看到ViewDragHelper的强大,强烈建议去了解下,这个是两个API的地址
ViewDraghelper
Callback
最后,附上源码链接
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。