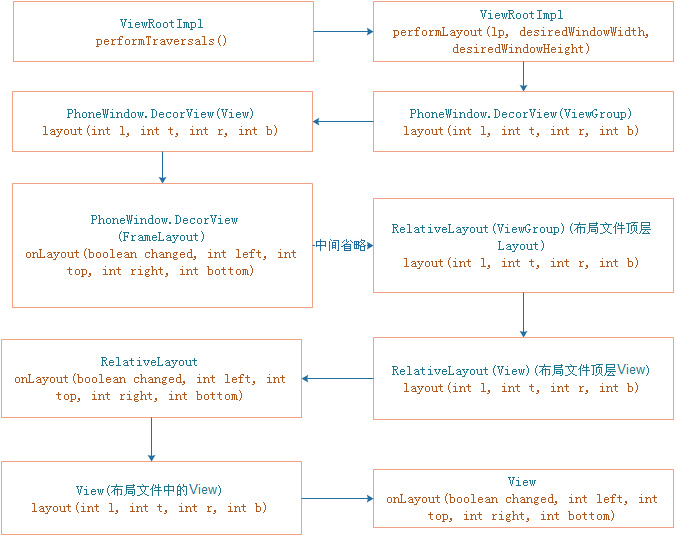
View布局最开始是从DecorView开始的,在ViewRootImpl中的performTraversals方法中,调用了 performLayout(lp, desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight),开始对DecorView测量:
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth, int desiredWindowHeight) { mLayoutRequested = false; mScrollMayChange = true; mInLayout = true; final View host = mView; if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION || DEBUG_LAYOUT) { Log.v(TAG, "Laying out " + host + " to (" + host.getMeasuredWidth() + ", " + host.getMeasuredHeight() + ")"); } Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "layout"); try { host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight()); mInLayout = false; int numViewsRequestingLayout = mLayoutRequesters.size(); if (numViewsRequestingLayout > 0) { // requestLayout() was called during layout. // If no layout-request flags are set on the requesting views, there is no problem. // If some requests are still pending, then we need to clear those flags and do // a full request/measure/layout pass to handle this situation. ArrayList<View> validLayoutRequesters = getValidLayoutRequesters(mLayoutRequesters, false); if (validLayoutRequesters != null) { // Set this flag to indicate that any further requests are happening during // the second pass, which may result in posting those requests to the next // frame instead mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest = true; // Process fresh layout requests, then measure and layout int numValidRequests = validLayoutRequesters.size(); for (int i = 0; i < numValidRequests; ++i) { final View view = validLayoutRequesters.get(i); Log.w("View", "requestLayout() improperly called by " + view + " during layout: running second layout pass"); view.requestLayout(); } measureHierarchy(host, lp, mView.getContext().getResources(), desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight); mInLayout = true; host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight()); mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest = false; // Check the valid requests again, this time without checking/clearing the // layout flags, since requests happening during the second pass get noop'd validLayoutRequesters = getValidLayoutRequesters(mLayoutRequesters, true); if (validLayoutRequesters != null) { final ArrayList<View> finalRequesters = validLayoutRequesters; // Post second-pass requests to the next frame getRunQueue().post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { int numValidRequests = finalRequesters.size(); for (int i = 0; i < numValidRequests; ++i) { final View view = finalRequesters.get(i); Log.w("View", "requestLayout() improperly called by " + view + " during second layout pass: posting in next frame"); view.requestLayout(); } } }); } } } } finally { Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW); } mInLayout = false; }15行,host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight()),调用的就是DecorView的layout方法,也就是View的layout方法:
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { if ((mPrivateFlags3 & PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT) != 0) { onMeasure(mOldWidthMeasureSpec, mOldHeightMeasureSpec); mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT; } int oldL = mLeft; int oldT = mTop; int oldB = mBottom; int oldR = mRight; boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ? setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b); if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) { onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED; ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo; if (li != null && li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners != null) { ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener> listenersCopy = (ArrayList<OnLayoutChangeListener>)li.mOnLayoutChangeListeners.clone(); int numListeners = listenersCopy.size(); for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) { listenersCopy.get(i).onLayoutChange(this, l, t, r, b, oldL, oldT, oldR, oldB); } } } mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT; mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_IS_LAID_OUT; }在调用layout方法传入了四个参数,分别是该View相对于父View左,上,有,下的位置。对于DecorView来说,就是相对于窗口的位置。那么这四个参数从哪里来的?
对于最顶层DecorView来说,就是由初始位置和在View Measure中获取的测量高度和测量宽度决定的。
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());对于子View,是由子View的测量宽度和测量高度和子View的LayoutParams决定的。
在layout方法13行,调用了setFrame方法:
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { boolean changed = false; if (DBG) { Log.d("View", this + " View.setFrame(" + left + "," + top + "," + right + "," + bottom + ")"); } if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) { changed = true; // Remember our drawn bit int drawn = mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWN; int oldWidth = mRight - mLeft; int oldHeight = mBottom - mTop; int newWidth = right - left; int newHeight = bottom - top; boolean sizeChanged = (newWidth != oldWidth) || (newHeight != oldHeight); // Invalidate our old position invalidate(sizeChanged); mLeft = left; mTop = top; mRight = right; mBottom = bottom; mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom); mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS; if (sizeChanged) { sizeChange(newWidth, newHeight, oldWidth, oldHeight); } if ((mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || mGhostView != null) { // If we are visible, force the DRAWN bit to on so that // this invalidate will go through (at least to our parent). // This is because someone may have invalidated this view // before this call to setFrame came in, thereby clearing // the DRAWN bit. mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN; invalidate(sizeChanged); // parent display list may need to be recreated based on a change in the bounds // of any child invalidateParentCaches(); } // Reset drawn bit to original value (invalidate turns it off) mPrivateFlags |= drawn; mBackgroundSizeChanged = true; notifySubtreeAccessibilityStateChangedIfNeeded(); } return changed; }在这个方法里面,完成对成员变量mLeft,mTop,mRight,mBottom的赋值,这些成员变量的值,将在View的绘制中用到。
在16行,调用 onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b)方法,DecorView没有重写这个方法,调用的是FrameLayout的onLayout方法:
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { layoutChildren(left, top, right, bottom, false /* no force left gravity */); }方法里面调用了layoutChildren方法:
void layoutChildren(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, boolean forceLeftGravity) { final int count = getChildCount(); final int parentLeft = getPaddingLeftWithForeground(); final int parentRight = right - left - getPaddingRightWithForeground(); final int parentTop = getPaddingTopWithForeground(); final int parentBottom = bottom - top - getPaddingBottomWithForeground(); mForegroundBoundsChanged = true; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = getChildAt(i); if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) { final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); final int width = child.getMeasuredWidth(); final int height = child.getMeasuredHeight(); int childLeft; int childTop; int gravity = lp.gravity; if (gravity == -1) { gravity = DEFAULT_CHILD_GRAVITY; } final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection(); final int absoluteGravity = Gravity.getAbsoluteGravity(gravity, layoutDirection); final int verticalGravity = gravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK; switch (absoluteGravity & Gravity.HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK) { case Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL: childLeft = parentLeft + (parentRight - parentLeft - width) / 2 + lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin; break; case Gravity.RIGHT: if (!forceLeftGravity) { childLeft = parentRight - width - lp.rightMargin; break; } case Gravity.LEFT: default: childLeft = parentLeft + lp.leftMargin; } switch (verticalGravity) { case Gravity.TOP: childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin; break; case Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL: childTop = parentTop + (parentBottom - parentTop - height) / 2 + lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin; break; case Gravity.BOTTOM: childTop = parentBottom - height - lp.bottomMargin; break; default: childTop = parentTop + lp.topMargin; } child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childLeft + width, childTop + height); } } }这里遍历所有的ViewView,计算每个子View相对于父View,左,上,右下的位置,然后调用子View的layout方法。
直到所有的View都完成测量。整个View测量的过程如下面的流程图所示:
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。